

Please note: reference image is displayed in place of Flash media.

Sinus rhythm is referred to as the “normal” heart rhythm. It represents the pattern of electrical activity that is seen on an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) when the heart is beating normally. An ECG is a routine test that records the electrical activity of the heart, using electrodes placed on the surface of the skin. A normal ECG has identifiable waves in each cycle that are named the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. The P wave is associated with activity in the atria (upper chambers of the heart); the QRS and T wave are associated with activity in the ventricles (lower chambers of the heart).
The electrical system of the heart is made up of several parts that communicate with one another to signal the heart muscle fibers to contract. The impulse is initiated by the sinoatrial node (SA node) which is located in the right atrium. The electrical impulse travels through the atria (causing them to contract) to the AV node and on through the bundle of His and the bundle branches located within the ventricles which causes the ventricles to contract. This flow of electrical signals produces a normal heartbeat or normal heart rhythm called “sinus rhythm.”
©2024 Medmovie.com. All rights reserved. Medmovie.com creates and licenses medical illustrations and animations for educational use. Our goal is to increase your understanding of medical terminology and help communication between patients, caregiver and healthcare professionals. The content in the Media Library is for your information and education purposes only. The Media Library is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment for specific medical conditions.
 3D Electrical MappingElectrical mapping of the heart is a procedure that is used to diagnose the origins of arrhythmias. This procedure uses…
3D Electrical MappingElectrical mapping of the heart is a procedure that is used to diagnose the origins of arrhythmias. This procedure uses… 3D Heart Ultrasound3D Heart Ultrasound provides your doctor with moving images of your heart and takes excellent pictures that will help…
3D Heart Ultrasound3D Heart Ultrasound provides your doctor with moving images of your heart and takes excellent pictures that will help… Active Fixation LeadAn active fixation lead is a pacemaker or implantable defibrillator lead that is fixed to the inside surface of the…
Active Fixation LeadAn active fixation lead is a pacemaker or implantable defibrillator lead that is fixed to the inside surface of the… AnginaAngina is the term used to describe a broad range symptoms due to blockages in the coronary arteries that reduce blood…
AnginaAngina is the term used to describe a broad range symptoms due to blockages in the coronary arteries that reduce blood…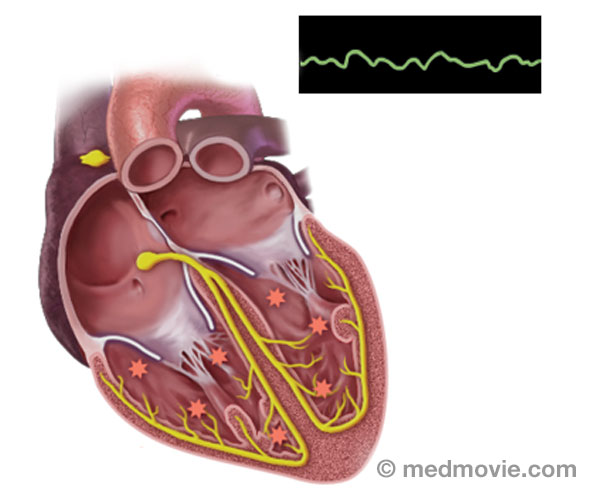 ArrhythmiasAn arrhythmia is a heartbeat that’s too fast, too slow or irregular (uneven). Arrhythmias are caused by problems with…
ArrhythmiasAn arrhythmia is a heartbeat that’s too fast, too slow or irregular (uneven). Arrhythmias are caused by problems with… AtherosclerosisAtherosclerosis is a disease that affects the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the organs of the…
AtherosclerosisAtherosclerosis is a disease that affects the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the organs of the… Atherosclerosis ComplicationsAtherosclerosis is a disease where fatty material called plaque builds up in the inner lining of arteries. Plaque…
Atherosclerosis ComplicationsAtherosclerosis is a disease where fatty material called plaque builds up in the inner lining of arteries. Plaque… Atrial FibrillationAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia with abnormal signals that originate in the atria of the heart.
The…
Atrial FibrillationAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia with abnormal signals that originate in the atria of the heart.
The…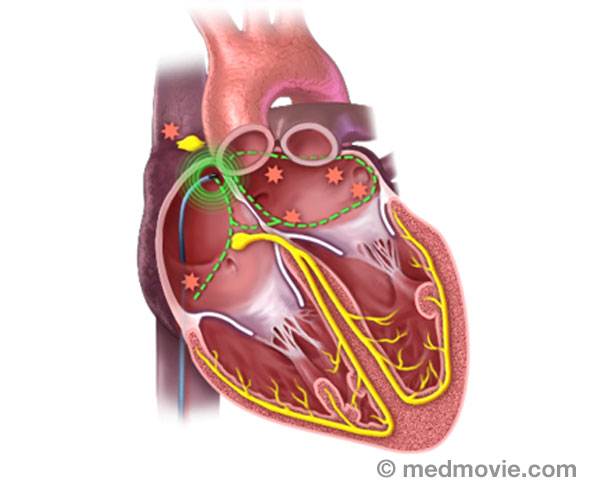 Atrial Fib. AblationAtrial fibrillation ablation is a procedure used to correct atrial fibrillation by destroying small areas of tissue…
Atrial Fib. AblationAtrial fibrillation ablation is a procedure used to correct atrial fibrillation by destroying small areas of tissue…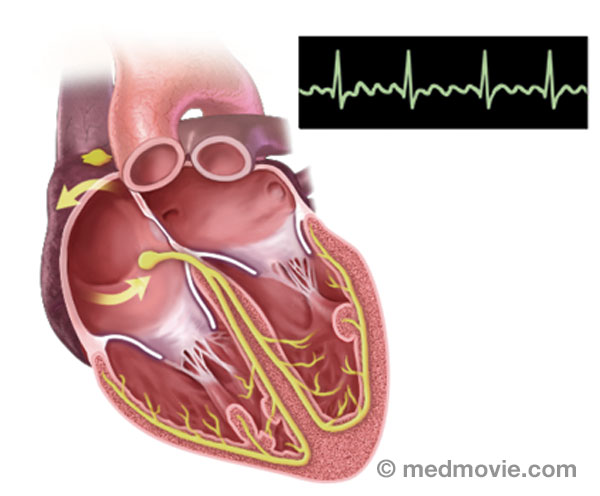 Atrial FlutterIn atrial flutter, electrical pulses that originate in the heart’s upper chambers and travel in a larger circuit. This…
Atrial FlutterIn atrial flutter, electrical pulses that originate in the heart’s upper chambers and travel in a larger circuit. This… Atrial Flutter AblationAtrial flutter ablation is a procedure used to correct atrial flutter by destroying small areas of tissue to block…
Atrial Flutter AblationAtrial flutter ablation is a procedure used to correct atrial flutter by destroying small areas of tissue to block… Atrial Septal DefectAtrial septal defect (ASD) is an abnormal opening in the septum, or wall, that separates the right and left atria. It…
Atrial Septal DefectAtrial septal defect (ASD) is an abnormal opening in the septum, or wall, that separates the right and left atria. It…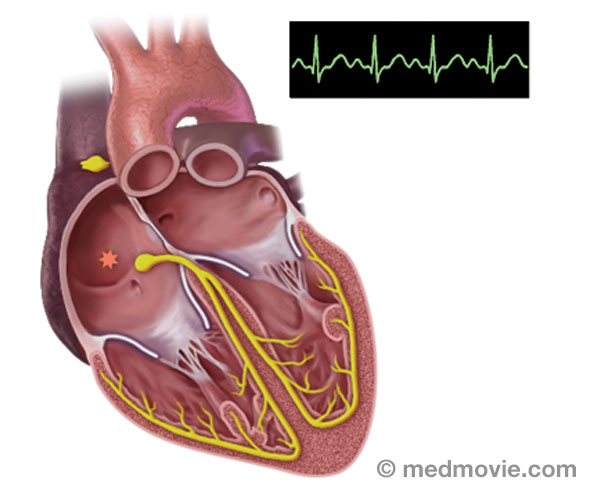 Atrial TachycardiaAtrial tachycardia is an abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia, that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical signals…
Atrial TachycardiaAtrial tachycardia is an abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia, that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical signals…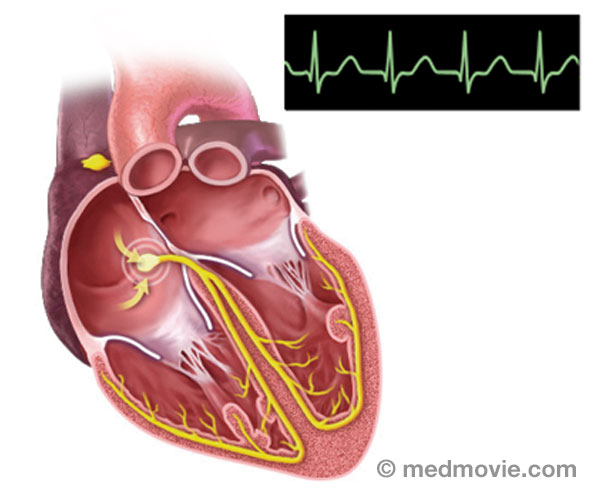 AVNRTAtrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT) is a heart arrhythmia with abnormal signals that reenter in the area…
AVNRTAtrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT) is a heart arrhythmia with abnormal signals that reenter in the area…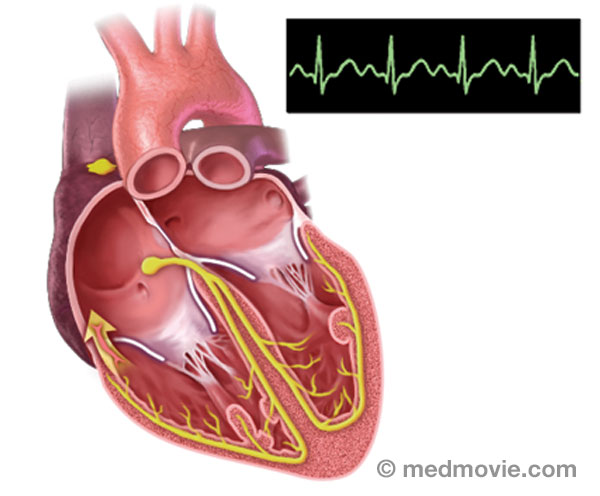 AVRTAtrioventricular Reentry Tachycardia (AVRT) or Wolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) is a condition in which the heart…
AVRTAtrioventricular Reentry Tachycardia (AVRT) or Wolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) is a condition in which the heart… AV Node AblationAV node ablation is a procedure used to correct irregular heartbeats by destroying the tissue within the AV node. AV…
AV Node AblationAV node ablation is a procedure used to correct irregular heartbeats by destroying the tissue within the AV node. AV… Blood ClotA blood clot is a normal reaction of the body that occurs if a vessel wall is injured. Blood clots are formed by a…
Blood ClotA blood clot is a normal reaction of the body that occurs if a vessel wall is injured. Blood clots are formed by a… Blood FlowBlood flows through the heart in a specific pattern. First blood returns from the lungs and body to the atria. It is…
Blood FlowBlood flows through the heart in a specific pattern. First blood returns from the lungs and body to the atria. It is…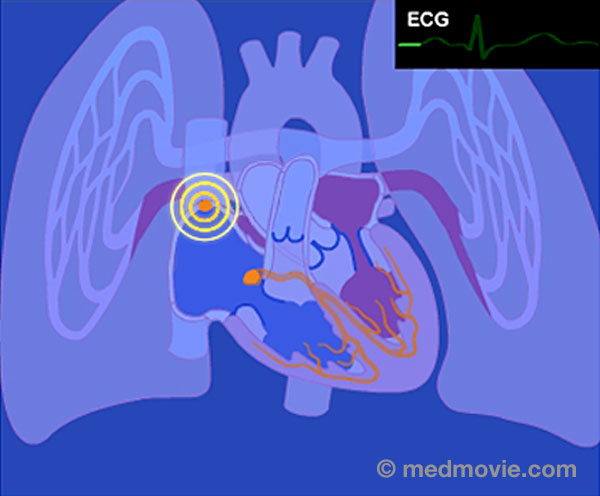 Blood Flow - ElectricThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to…
Blood Flow - ElectricThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to…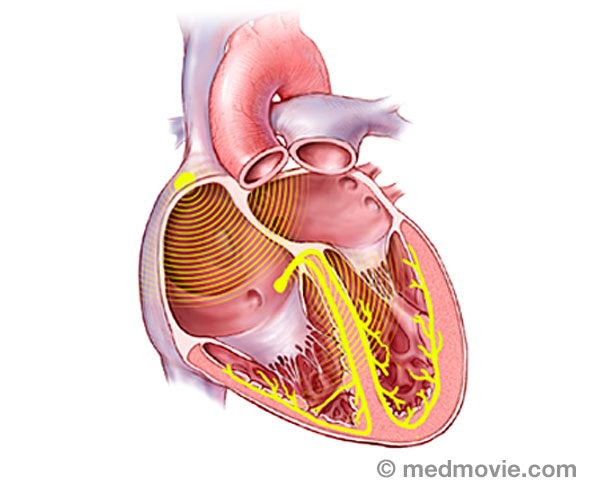 Bundle BranchesThe bundle branches are part of the normal electrical system of the heart. The electrical impulse that causes the heart…
Bundle BranchesThe bundle branches are part of the normal electrical system of the heart. The electrical impulse that causes the heart…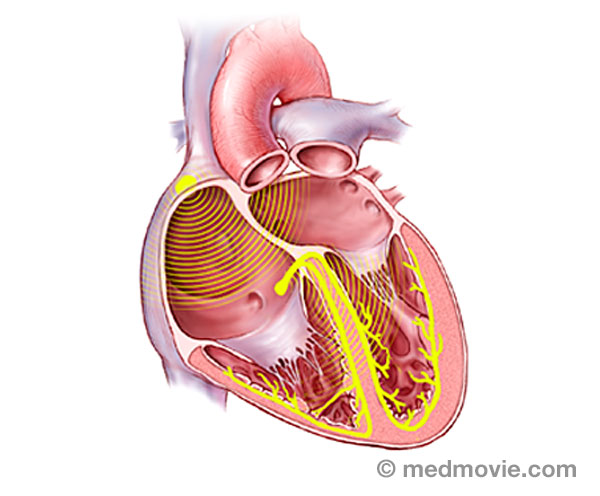 Bundle of HisThe bundle of His is part of the heart’s electrical system. It is a collection of cells that carry electrical signals…
Bundle of HisThe bundle of His is part of the heart’s electrical system. It is a collection of cells that carry electrical signals…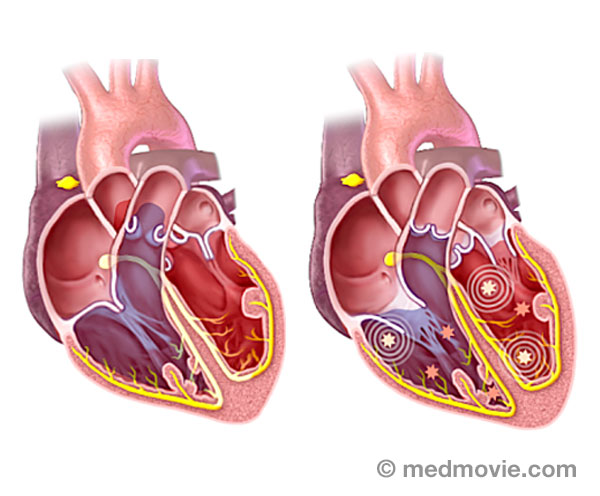 Cardiac ArrestSudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is an event caused by a problem with the heart’s “electrical” system. SCA occurs when the…
Cardiac ArrestSudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is an event caused by a problem with the heart’s “electrical” system. SCA occurs when the…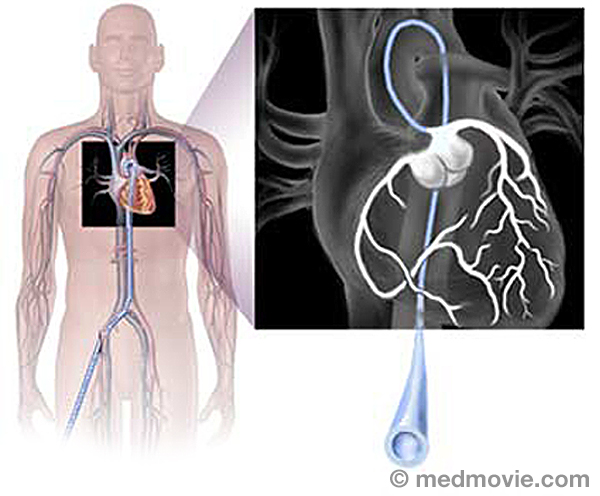 Cardiac CatheterizationCardiac catheterization, commonly called a “cardiac cath ”, is a procedure used to evaluate multiple aspects of the…
Cardiac CatheterizationCardiac catheterization, commonly called a “cardiac cath ”, is a procedure used to evaluate multiple aspects of the…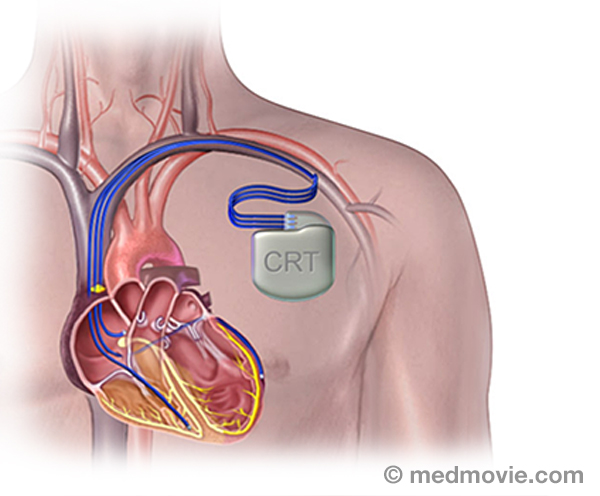 CRT DeviceA cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your…
CRT DeviceA cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your…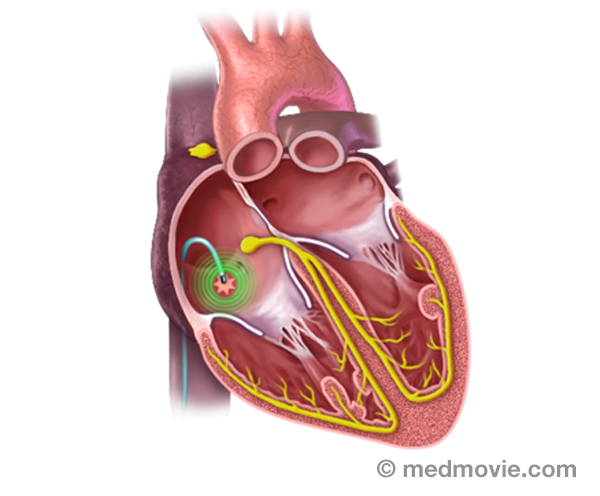 Catheter AblationThe electrical system of the heart controls each heartbeat. Electrical impulses generated by special tissue (nodes)…
Catheter AblationThe electrical system of the heart controls each heartbeat. Electrical impulses generated by special tissue (nodes)… Heart ChambersThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria, specifically the right atrium and the…
Heart ChambersThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria, specifically the right atrium and the…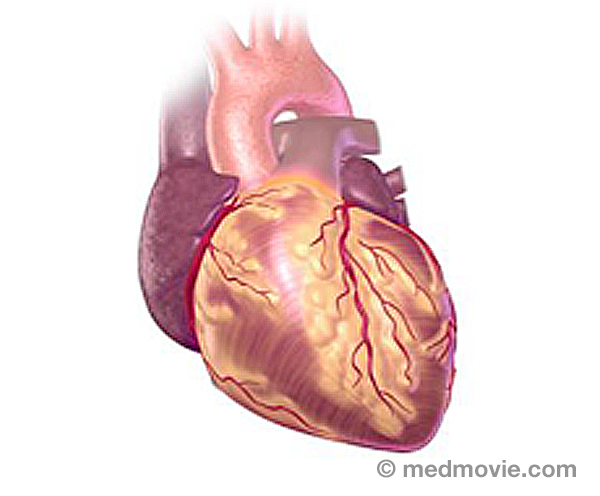 Common Heart ProblemsSudden cardiac arrest, heart attack, heart failure, heart valve disease- these are all terms that are common to…
Common Heart ProblemsSudden cardiac arrest, heart attack, heart failure, heart valve disease- these are all terms that are common to…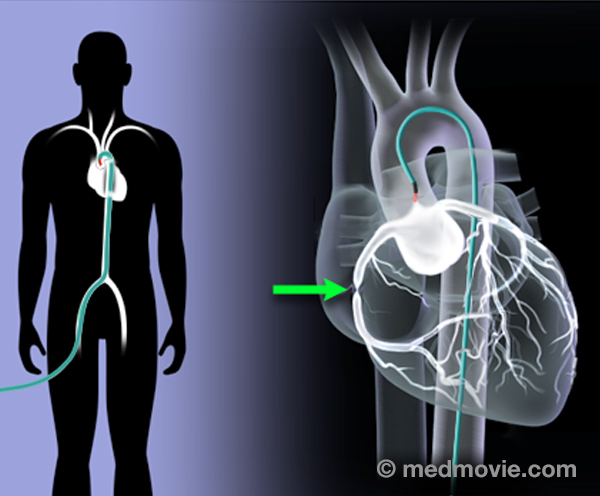 Coronary AngiogramAn angiogram is a test that takes X-ray pictures of blood vessels while injecting X-ray contrast (“dye”). A coronary…
Coronary AngiogramAn angiogram is a test that takes X-ray pictures of blood vessels while injecting X-ray contrast (“dye”). A coronary… Coronary AngioplastyCoronary angioplasty (PTCA) is a procedure that opens up narrowed or blocked segments of the arteries that supply blood…
Coronary AngioplastyCoronary angioplasty (PTCA) is a procedure that opens up narrowed or blocked segments of the arteries that supply blood…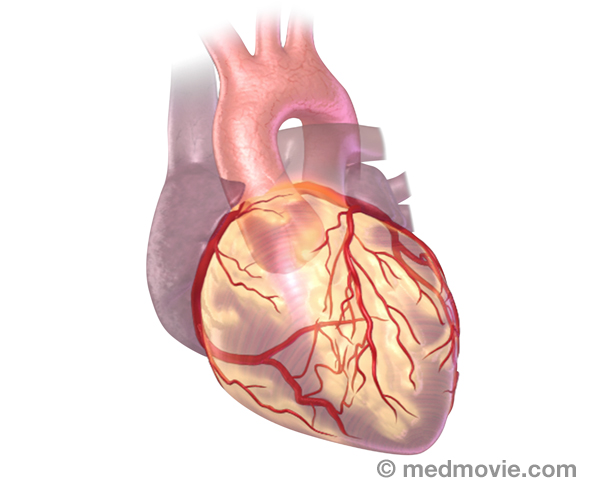 Coronary ArteriesThe coronary arteries are the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle. They branch off of the aorta at its…
Coronary ArteriesThe coronary arteries are the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle. They branch off of the aorta at its…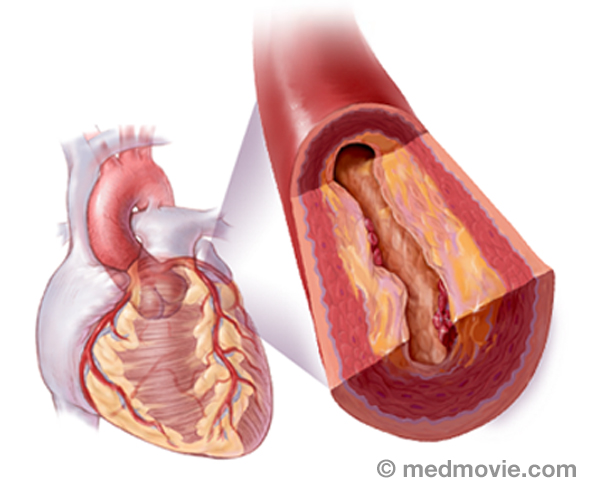 Coronary Artery DiseaseCoronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to your heart muscle become narrowed or blocked by…
Coronary Artery DiseaseCoronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to your heart muscle become narrowed or blocked by…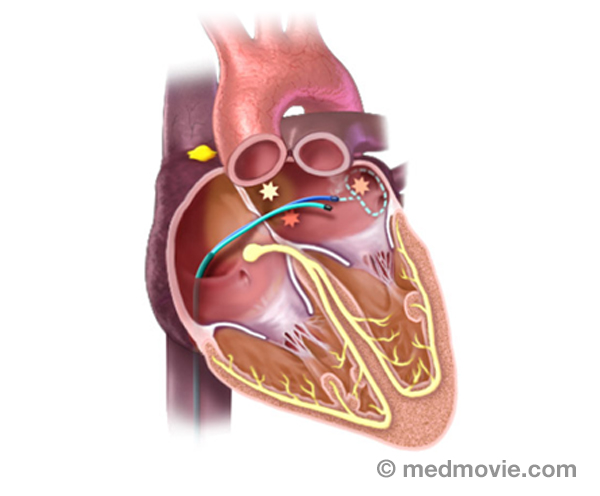 CryotherapyCryotherapy is a procedure that can be used to treat arrhythmias in the heart. This procedure uses a special catheter…
CryotherapyCryotherapy is a procedure that can be used to treat arrhythmias in the heart. This procedure uses a special catheter… Device MonitoringDevice monitoring is a technique used to track the activity of the heart and an ICD or pacemaker. This can be performed…
Device MonitoringDevice monitoring is a technique used to track the activity of the heart and an ICD or pacemaker. This can be performed… Ebstein SyndromeEbstein syndrome is characterized by a severely malformed and displaced tricuspid valve. This results in regurgitation,…
Ebstein SyndromeEbstein syndrome is characterized by a severely malformed and displaced tricuspid valve. This results in regurgitation,…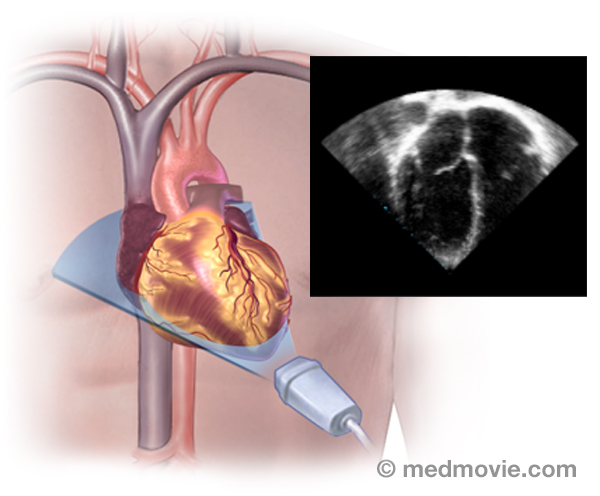 EchocardiogramAn echocardiogram is a procedure that uses ultrasound waves to create moving pictures of the heart structures, and…
EchocardiogramAn echocardiogram is a procedure that uses ultrasound waves to create moving pictures of the heart structures, and… Ejection FractionDuring each heartbeat, the heart contracts and relaxes. The ventricles are the pumping chambers of the heart. In…
Ejection FractionDuring each heartbeat, the heart contracts and relaxes. The ventricles are the pumping chambers of the heart. In…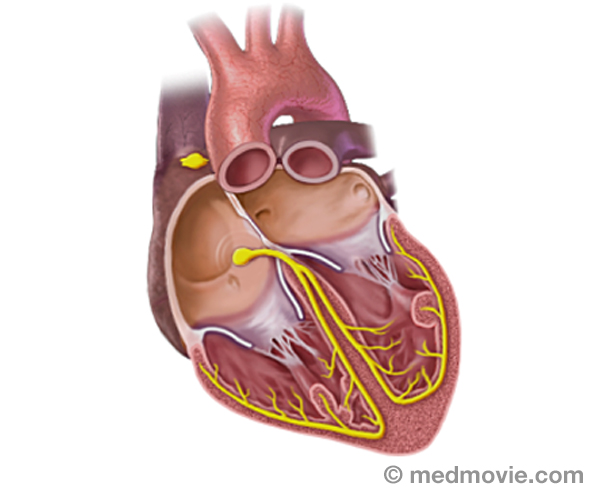 Electrical SystemThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to…
Electrical SystemThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to… ElectrocardiogramAn electrocardiogram, ECG or EKG, is a quick, painless test that records the electrical activity of the heart. Small…
ElectrocardiogramAn electrocardiogram, ECG or EKG, is a quick, painless test that records the electrical activity of the heart. Small…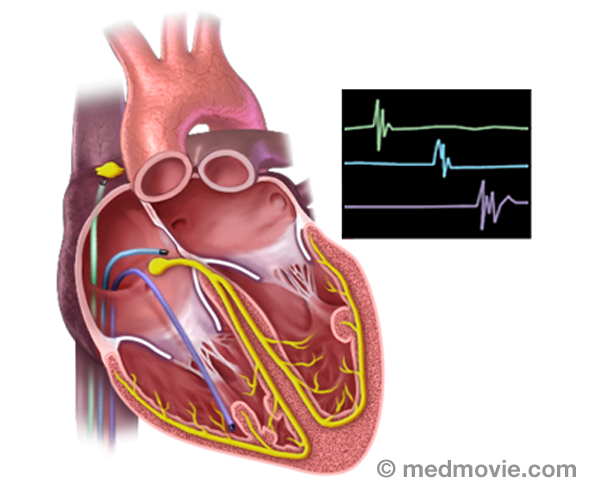 Electrophysiology StudyAn electrophysiology study is performed to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart.
The purpose of the…
Electrophysiology StudyAn electrophysiology study is performed to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart.
The purpose of the…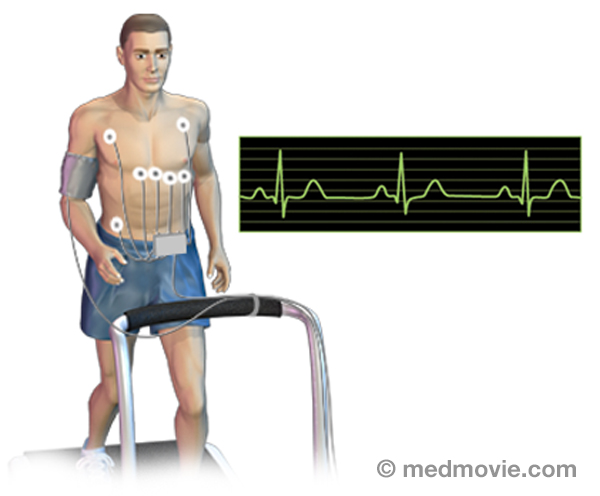 Exercise Stress TestAn exercise stress test is a diagnostic test in which a person walks on a treadmill or pedals a stationary bicycle…
Exercise Stress TestAn exercise stress test is a diagnostic test in which a person walks on a treadmill or pedals a stationary bicycle…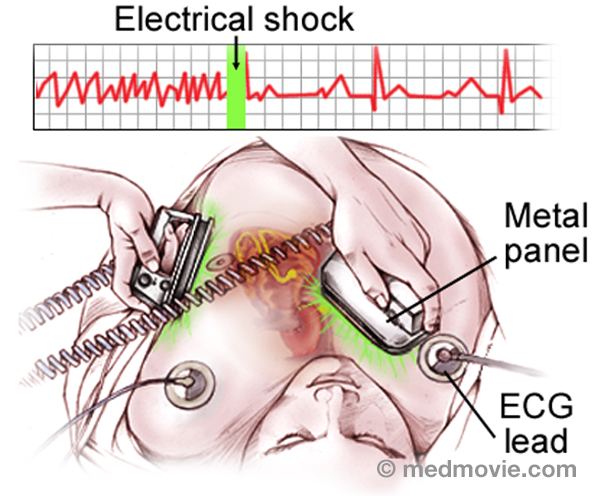 External DefibrillatorAn external defibrillator is a machine that is used to deliver an electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal…
External DefibrillatorAn external defibrillator is a machine that is used to deliver an electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal…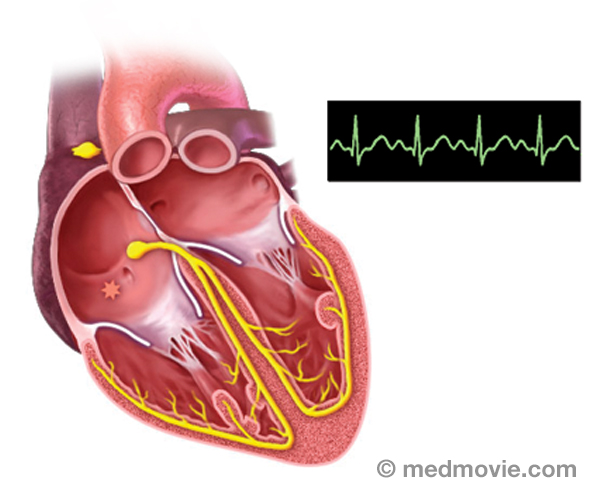 Atrial Tachycardia - FocalFocal atrial tachycardia is an abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia, that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…
Atrial Tachycardia - FocalFocal atrial tachycardia is an abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia, that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical… Ventricular Tachycardia FocalFocal ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…
Ventricular Tachycardia FocalFocal ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…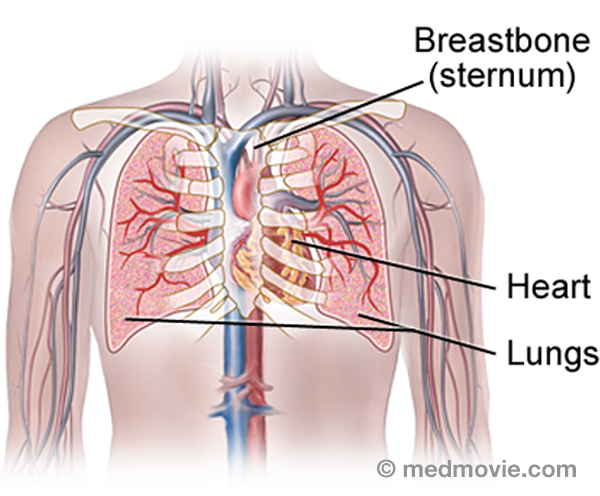 Heart and LungsThe heart can be thought of as the main pump within the circulatory system. The right side of the heart collects blood…
Heart and LungsThe heart can be thought of as the main pump within the circulatory system. The right side of the heart collects blood…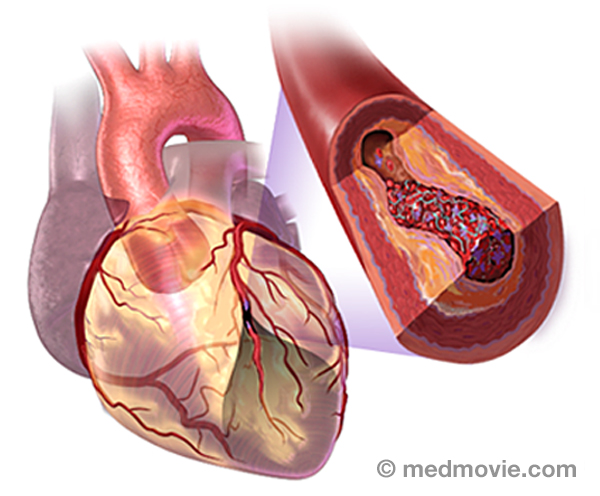 Heart AttackA heart attack, also referred to as a “myocardial infarction or MI”, occurs when the flow of blood and oxygen to an…
Heart AttackA heart attack, also referred to as a “myocardial infarction or MI”, occurs when the flow of blood and oxygen to an…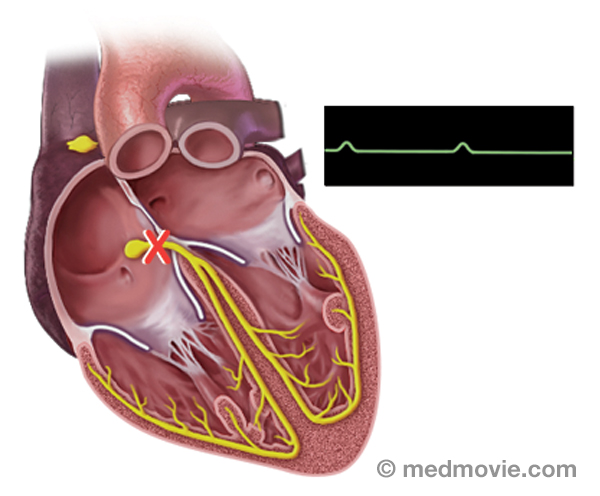 Heart BlockHeart block is an arrhythmia (or “abnormal heart rhythm) in which electrical signals traveling from the atria to the…
Heart BlockHeart block is an arrhythmia (or “abnormal heart rhythm) in which electrical signals traveling from the atria to the… Heart FailureHeart failure is the term used to describe many conditions of the heart that lead to symptoms such as breathlessness,…
Heart FailureHeart failure is the term used to describe many conditions of the heart that lead to symptoms such as breathlessness,…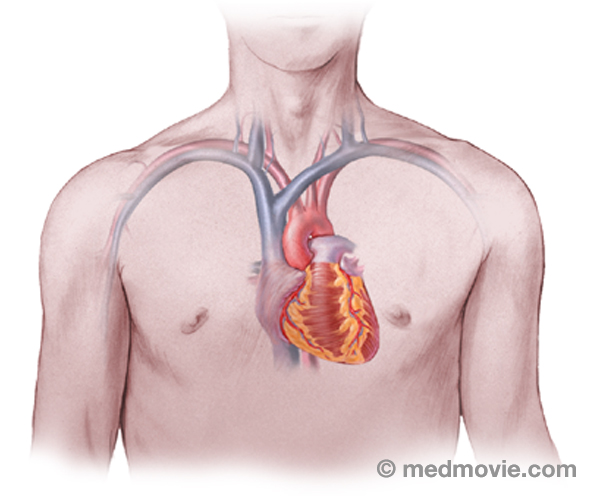 Heart LocationThe heart is located within the rib cage, under and slightly to the left of the breastbone (sternum). It approximately…
Heart LocationThe heart is located within the rib cage, under and slightly to the left of the breastbone (sternum). It approximately… Heart TransplantA heart transplant is a surgical procedure that replaces a failing heart with a healthy donor heart. Physicians make a…
Heart TransplantA heart transplant is a surgical procedure that replaces a failing heart with a healthy donor heart. Physicians make a…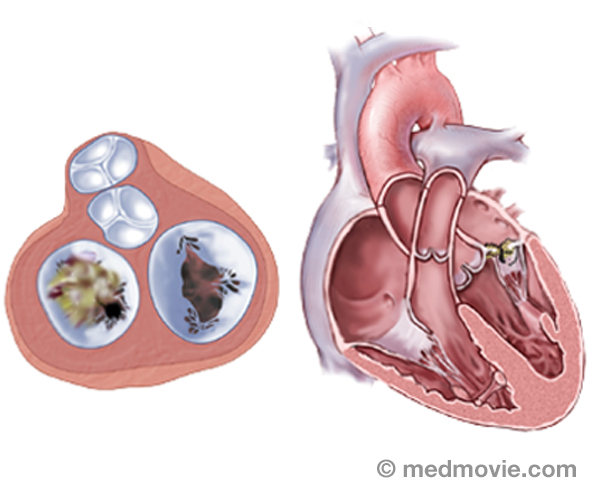 Heart Valve DiseaseValvular heart disease is any condition that disrupts the proper function of the valve. There are four valves in the…
Heart Valve DiseaseValvular heart disease is any condition that disrupts the proper function of the valve. There are four valves in the… Heart Valve SurgeryHeart valve replacement surgery replaces an abnormal or diseased heart valve with a healthy one. The replacement valve…
Heart Valve SurgeryHeart valve replacement surgery replaces an abnormal or diseased heart valve with a healthy one. The replacement valve… High Blood PresureHigh blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition in which blood pressure levels are measured above the normal…
High Blood PresureHigh blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition in which blood pressure levels are measured above the normal… HBP ComplicationsBlood pressure is a measurement that reflects the pressure within the arteries. When the heart pumps, the higher…
HBP ComplicationsBlood pressure is a measurement that reflects the pressure within the arteries. When the heart pumps, the higher…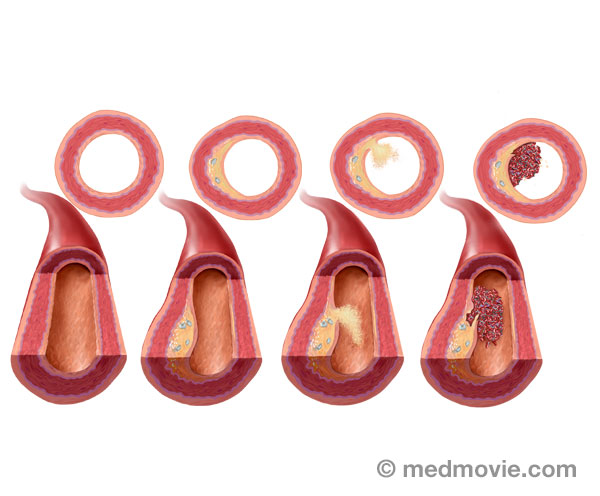 High CholesterolCholesterol is a fatty type substance produced by the body and absorbed from the food you eat. Some cholesterol is…
High CholesterolCholesterol is a fatty type substance produced by the body and absorbed from the food you eat. Some cholesterol is…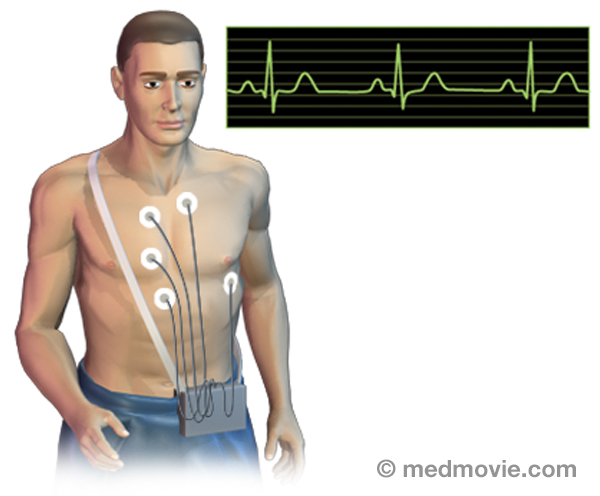 Holter MonitorA Holter monitor is a battery-operated, portable device that measures and tape-records your heart’s electrical activity…
Holter MonitorA Holter monitor is a battery-operated, portable device that measures and tape-records your heart’s electrical activity…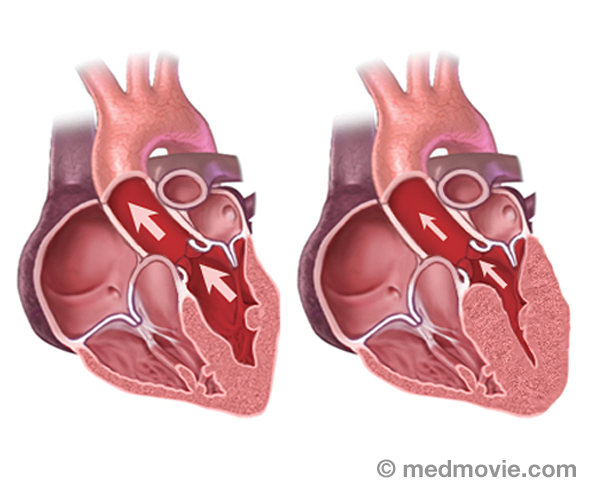 Cardiomyopathy HypertrophicHypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle in which the wall of the heart, particularly the muscular…
Cardiomyopathy HypertrophicHypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle in which the wall of the heart, particularly the muscular…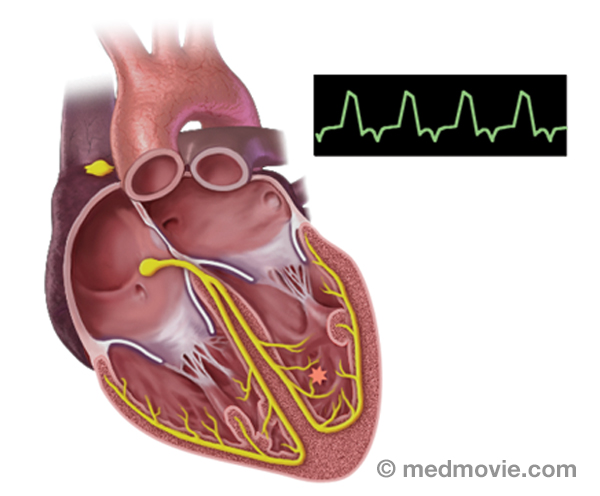 Ventric. Tachy. IdiopathicIdiopathic ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…
Ventric. Tachy. IdiopathicIdiopathic ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical… ICD DeviceAn implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a battery-powered device placed under your skin, beneath the…
ICD DeviceAn implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a battery-powered device placed under your skin, beneath the…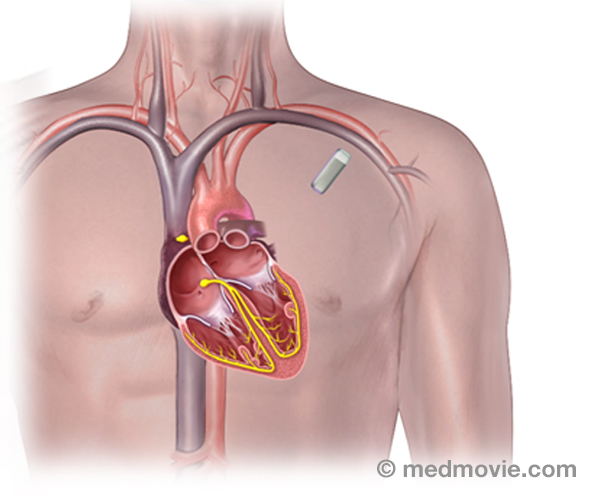 Loop RecorderAn implantable loop recorder is a small device that is implanted under the skin to help identify the causes of…
Loop RecorderAn implantable loop recorder is a small device that is implanted under the skin to help identify the causes of…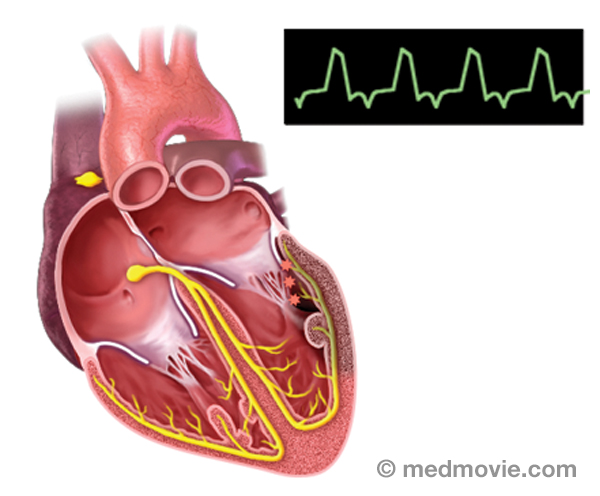 Ventric. Tach. Ischem. TachycardiaIschemic Ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…
Ventric. Tach. Ischem. TachycardiaIschemic Ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…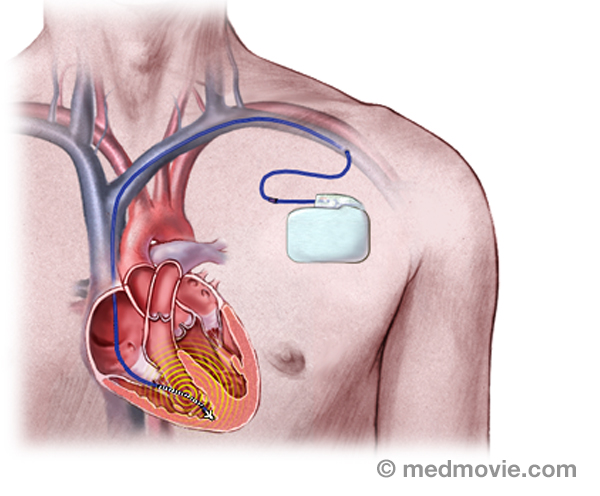 LeadA lead is a device that allows the passage of electrical signals. Leads are used in electrocardiograms to record the…
LeadA lead is a device that allows the passage of electrical signals. Leads are used in electrocardiograms to record the… Long QT SyndromeLong QT Syndrome is a condition that is characterized by a delay in repolarization of the heart after the initial…
Long QT SyndromeLong QT Syndrome is a condition that is characterized by a delay in repolarization of the heart after the initial… Mitral ValveThe mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. It allows blood to flow from the…
Mitral ValveThe mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. It allows blood to flow from the… Mitral StenosisThe mitral valve is the heart valve located between the left atrium (top chamber) and left ventricle (bottom chamber…
Mitral StenosisThe mitral valve is the heart valve located between the left atrium (top chamber) and left ventricle (bottom chamber… PacemakersA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or…
PacemakersA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or… Pacemakers - DualA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or…
Pacemakers - DualA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or…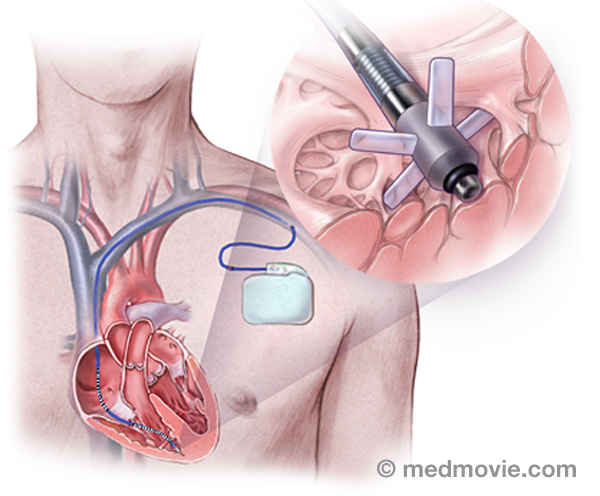 Passive Fixation LeadA passive fixation lead is a type of pacemaker or defibrillator “wire” that is used to send the electrical signal of…
Passive Fixation LeadA passive fixation lead is a type of pacemaker or defibrillator “wire” that is used to send the electrical signal of…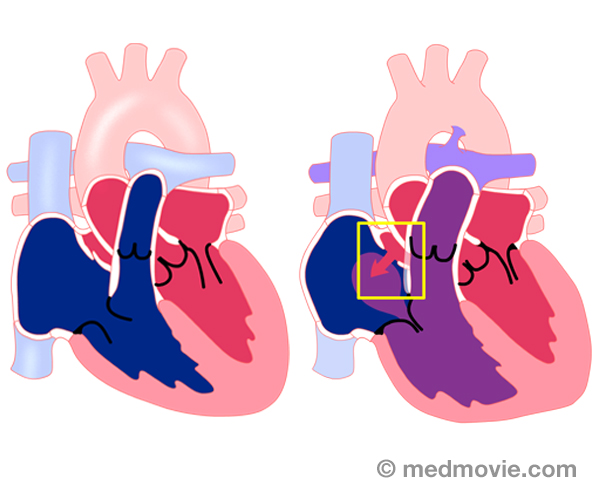 Patent Foramen OvalePatent Foramen Ovale, or PFO, is a hole in the septum that separates the upper chambers of the heart. This hole is…
Patent Foramen OvalePatent Foramen Ovale, or PFO, is a hole in the septum that separates the upper chambers of the heart. This hole is… PVCPremature ventricular contraction (PVC) is an abnormal heartbeat in which the ventricle contracts early without…
PVCPremature ventricular contraction (PVC) is an abnormal heartbeat in which the ventricle contracts early without…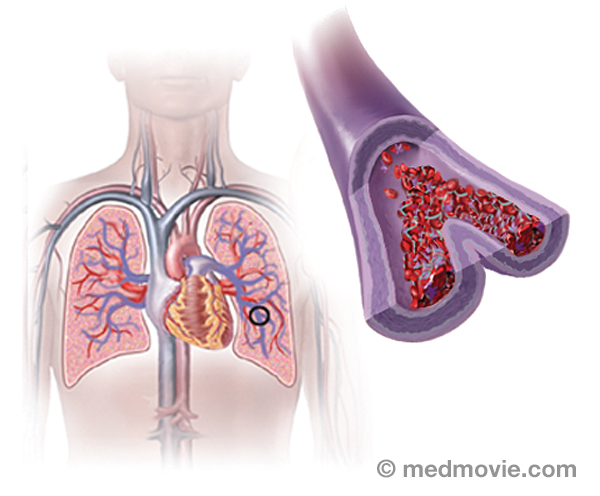 Pulmonary EmbolismA pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that had “traveled” to the lungs, most commonly from blood clots in the legs. The…
Pulmonary EmbolismA pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that had “traveled” to the lungs, most commonly from blood clots in the legs. The…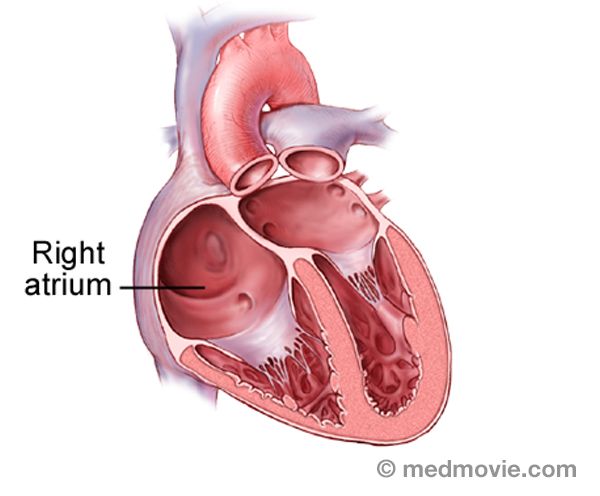 Right AtriumThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria, and are separated into the right and…
Right AtriumThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria, and are separated into the right and… Ventric. Tach. RVOT.Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Ventricular Tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal…
Ventric. Tach. RVOT.Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Ventricular Tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal… Single VentricleSingle ventricle is a birth defect in which one lower chamber (ventricle) of the heart is abnormally small…
Single VentricleSingle ventricle is a birth defect in which one lower chamber (ventricle) of the heart is abnormally small…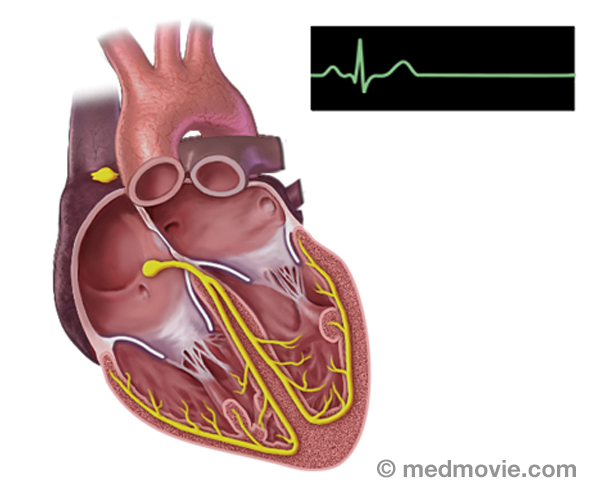 Sinus BradycardiaSinus bradycardia is a condition in which the heart beats too slowly (less than 60 beats per minute). It may be caused…
Sinus BradycardiaSinus bradycardia is a condition in which the heart beats too slowly (less than 60 beats per minute). It may be caused… Sinus TachycardiaSinus tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat that is caused by a sino-atrial node that fires too rapidly.
The electrical…
Sinus TachycardiaSinus tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat that is caused by a sino-atrial node that fires too rapidly.
The electrical… Smoking CessationSmoking cessation refers to quitting smoking. Quitting smoking is not easy, but there are things you can do to increase…
Smoking CessationSmoking cessation refers to quitting smoking. Quitting smoking is not easy, but there are things you can do to increase…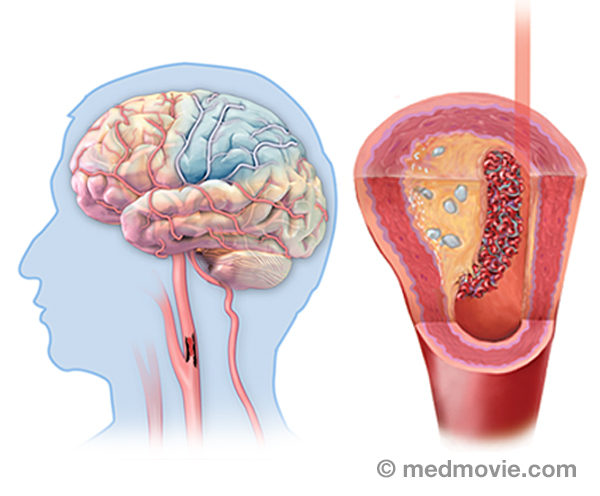 StrokeStroke results from the sudden loss of blood flow to the brain, usually a specific part of the brain. The brain needs a…
StrokeStroke results from the sudden loss of blood flow to the brain, usually a specific part of the brain. The brain needs a…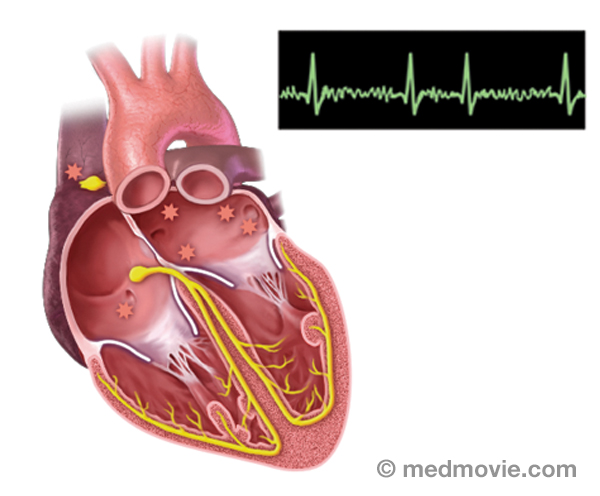 SVTThe electrical system of the heart is made up of several parts that communicate with one another to signal the heart…
SVTThe electrical system of the heart is made up of several parts that communicate with one another to signal the heart…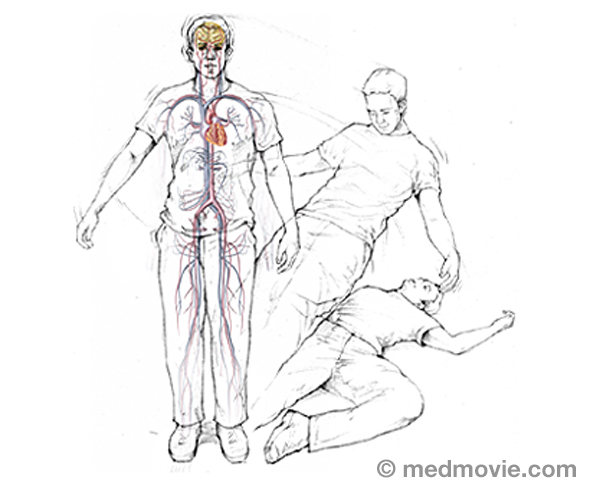 SyncopeSyncope (or fainting) is a temporary loss of consciousness, with the inability to maintain postural tone. When patients…
SyncopeSyncope (or fainting) is a temporary loss of consciousness, with the inability to maintain postural tone. When patients…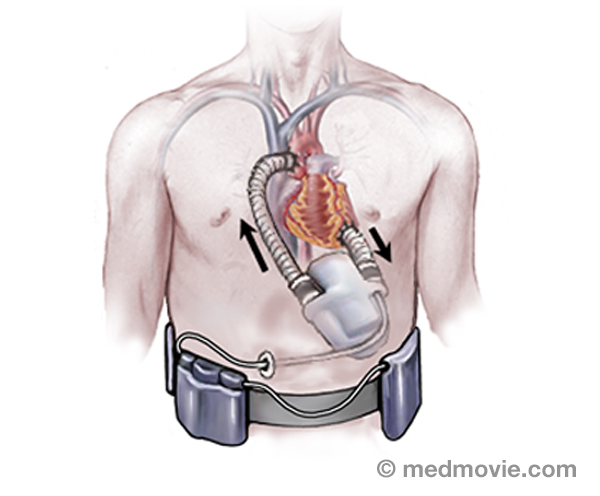 Ventric. Assist DeviceA ventricular assist device is a pumping device that is used to help a heart that can no longer pump blood effectively…
Ventric. Assist DeviceA ventricular assist device is a pumping device that is used to help a heart that can no longer pump blood effectively… Ventric. FibrillationVentricular fibrillation is a very fast, irregular heartbeat that is caused by abnormal firing of electrical signals in…
Ventric. FibrillationVentricular fibrillation is a very fast, irregular heartbeat that is caused by abnormal firing of electrical signals in…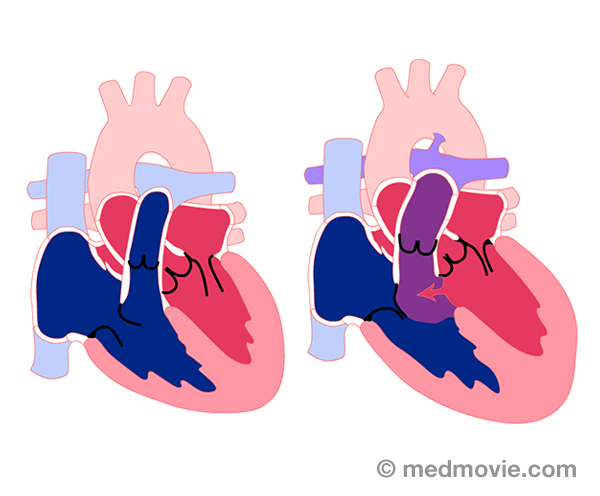 Ventric. Septal DefectVentricular septal defect, or VSD, is a hole in the wall or septum that separates the right and left lower chambers…
Ventric. Septal DefectVentricular septal defect, or VSD, is a hole in the wall or septum that separates the right and left lower chambers…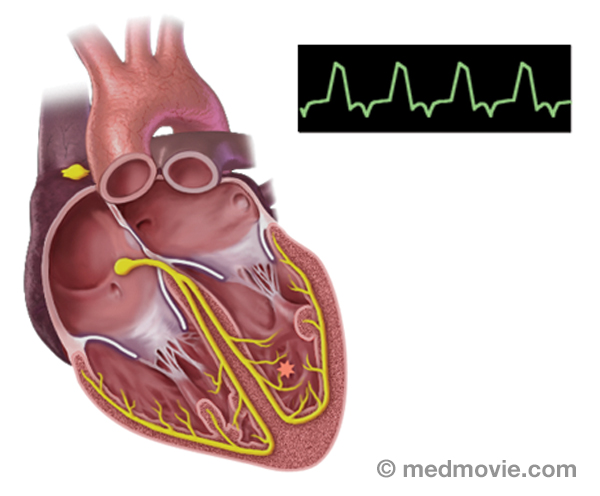 Ventric. TachycardiaVentricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical signals in…
Ventric. TachycardiaVentricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical signals in… Ventric. Tach. AblationVentricular tachycardia ablation is a procedure used to correct ventricular tachycardia by destroying the tissue that…
Ventric. Tach. AblationVentricular tachycardia ablation is a procedure used to correct ventricular tachycardia by destroying the tissue that… Wolff-Parkinson WhiteWolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) is a condition in which the heart beats too fast due to abnormal, extra electrical…
Wolff-Parkinson WhiteWolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) is a condition in which the heart beats too fast due to abnormal, extra electrical… 3D Electrical MappingElectrical mapping of the heart is a procedure that is used to diagnose the origins of arrhythmias. This procedure uses…
3D Electrical MappingElectrical mapping of the heart is a procedure that is used to diagnose the origins of arrhythmias. This procedure uses… 3D Heart Ultrasound3D Heart Ultrasound provides your doctor with moving images of your heart and takes excellent pictures that will help…
3D Heart Ultrasound3D Heart Ultrasound provides your doctor with moving images of your heart and takes excellent pictures that will help… Active Fixation LeadAn active fixation lead is a pacemaker or implantable defibrillator lead that is fixed to the inside surface of the…
Active Fixation LeadAn active fixation lead is a pacemaker or implantable defibrillator lead that is fixed to the inside surface of the… AnginaAngina is the term used to describe a broad range symptoms due to blockages in the coronary arteries that reduce blood…
AnginaAngina is the term used to describe a broad range symptoms due to blockages in the coronary arteries that reduce blood… ArrhythmiasAn arrhythmia is a heartbeat that’s too fast, too slow or irregular (uneven). Arrhythmias are caused by problems with…
ArrhythmiasAn arrhythmia is a heartbeat that’s too fast, too slow or irregular (uneven). Arrhythmias are caused by problems with… AtherosclerosisAtherosclerosis is a disease that affects the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the organs of the…
AtherosclerosisAtherosclerosis is a disease that affects the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the organs of the… Atherosclerosis ComplicationsAtherosclerosis is a disease where fatty material called plaque builds up in the inner lining of arteries. Plaque…
Atherosclerosis ComplicationsAtherosclerosis is a disease where fatty material called plaque builds up in the inner lining of arteries. Plaque… Atrial FibrillationAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia with abnormal signals that originate in the atria of the heart.
The…
Atrial FibrillationAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia with abnormal signals that originate in the atria of the heart.
The… Atrial Fib. AblationAtrial fibrillation ablation is a procedure used to correct atrial fibrillation by destroying small areas of tissue…
Atrial Fib. AblationAtrial fibrillation ablation is a procedure used to correct atrial fibrillation by destroying small areas of tissue… Atrial FlutterIn atrial flutter, electrical pulses that originate in the heart’s upper chambers and travel in a larger circuit. This…
Atrial FlutterIn atrial flutter, electrical pulses that originate in the heart’s upper chambers and travel in a larger circuit. This… Atrial Flutter AblationAtrial flutter ablation is a procedure used to correct atrial flutter by destroying small areas of tissue to block…
Atrial Flutter AblationAtrial flutter ablation is a procedure used to correct atrial flutter by destroying small areas of tissue to block… Atrial Septal DefectAtrial septal defect (ASD) is an abnormal opening in the septum, or wall, that separates the right and left atria. It…
Atrial Septal DefectAtrial septal defect (ASD) is an abnormal opening in the septum, or wall, that separates the right and left atria. It… Atrial TachycardiaAtrial tachycardia is an abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia, that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical signals…
Atrial TachycardiaAtrial tachycardia is an abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia, that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical signals… AVNRTAtrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT) is a heart arrhythmia with abnormal signals that reenter in the area…
AVNRTAtrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT) is a heart arrhythmia with abnormal signals that reenter in the area… AVRTAtrioventricular Reentry Tachycardia (AVRT) or Wolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) is a condition in which the heart…
AVRTAtrioventricular Reentry Tachycardia (AVRT) or Wolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) is a condition in which the heart… AV Node AblationAV node ablation is a procedure used to correct irregular heartbeats by destroying the tissue within the AV node. AV…
AV Node AblationAV node ablation is a procedure used to correct irregular heartbeats by destroying the tissue within the AV node. AV… Blood ClotA blood clot is a normal reaction of the body that occurs if a vessel wall is injured. Blood clots are formed by a…
Blood ClotA blood clot is a normal reaction of the body that occurs if a vessel wall is injured. Blood clots are formed by a… Blood FlowBlood flows through the heart in a specific pattern. First blood returns from the lungs and body to the atria. It is…
Blood FlowBlood flows through the heart in a specific pattern. First blood returns from the lungs and body to the atria. It is… Blood Flow - ElectricThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to…
Blood Flow - ElectricThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to… Bundle BranchesThe bundle branches are part of the normal electrical system of the heart. The electrical impulse that causes the heart…
Bundle BranchesThe bundle branches are part of the normal electrical system of the heart. The electrical impulse that causes the heart… Bundle of HisThe bundle of His is part of the heart’s electrical system. It is a collection of cells that carry electrical signals…
Bundle of HisThe bundle of His is part of the heart’s electrical system. It is a collection of cells that carry electrical signals… Cardiac ArrestSudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is an event caused by a problem with the heart’s “electrical” system. SCA occurs when the…
Cardiac ArrestSudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is an event caused by a problem with the heart’s “electrical” system. SCA occurs when the… Cardiac CatheterizationCardiac catheterization, commonly called a “cardiac cath ”, is a procedure used to evaluate multiple aspects of the…
Cardiac CatheterizationCardiac catheterization, commonly called a “cardiac cath ”, is a procedure used to evaluate multiple aspects of the… CRT DeviceA cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your…
CRT DeviceA cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your… Catheter AblationThe electrical system of the heart controls each heartbeat. Electrical impulses generated by special tissue (nodes)…
Catheter AblationThe electrical system of the heart controls each heartbeat. Electrical impulses generated by special tissue (nodes)… Heart ChambersThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria, specifically the right atrium and the…
Heart ChambersThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria, specifically the right atrium and the… Common Heart ProblemsSudden cardiac arrest, heart attack, heart failure, heart valve disease- these are all terms that are common to…
Common Heart ProblemsSudden cardiac arrest, heart attack, heart failure, heart valve disease- these are all terms that are common to… Coronary AngiogramAn angiogram is a test that takes X-ray pictures of blood vessels while injecting X-ray contrast (“dye”). A coronary…
Coronary AngiogramAn angiogram is a test that takes X-ray pictures of blood vessels while injecting X-ray contrast (“dye”). A coronary… Coronary AngioplastyCoronary angioplasty (PTCA) is a procedure that opens up narrowed or blocked segments of the arteries that supply blood…
Coronary AngioplastyCoronary angioplasty (PTCA) is a procedure that opens up narrowed or blocked segments of the arteries that supply blood… Coronary ArteriesThe coronary arteries are the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle. They branch off of the aorta at its…
Coronary ArteriesThe coronary arteries are the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle. They branch off of the aorta at its… Coronary Artery DiseaseCoronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to your heart muscle become narrowed or blocked by…
Coronary Artery DiseaseCoronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to your heart muscle become narrowed or blocked by… CryotherapyCryotherapy is a procedure that can be used to treat arrhythmias in the heart. This procedure uses a special catheter…
CryotherapyCryotherapy is a procedure that can be used to treat arrhythmias in the heart. This procedure uses a special catheter… Device MonitoringDevice monitoring is a technique used to track the activity of the heart and an ICD or pacemaker. This can be performed…
Device MonitoringDevice monitoring is a technique used to track the activity of the heart and an ICD or pacemaker. This can be performed… Ebstein SyndromeEbstein syndrome is characterized by a severely malformed and displaced tricuspid valve. This results in regurgitation,…
Ebstein SyndromeEbstein syndrome is characterized by a severely malformed and displaced tricuspid valve. This results in regurgitation,… EchocardiogramAn echocardiogram is a procedure that uses ultrasound waves to create moving pictures of the heart structures, and…
EchocardiogramAn echocardiogram is a procedure that uses ultrasound waves to create moving pictures of the heart structures, and… Ejection FractionDuring each heartbeat, the heart contracts and relaxes. The ventricles are the pumping chambers of the heart. In…
Ejection FractionDuring each heartbeat, the heart contracts and relaxes. The ventricles are the pumping chambers of the heart. In… Electrical SystemThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to…
Electrical SystemThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to… ElectrocardiogramAn electrocardiogram, ECG or EKG, is a quick, painless test that records the electrical activity of the heart. Small…
ElectrocardiogramAn electrocardiogram, ECG or EKG, is a quick, painless test that records the electrical activity of the heart. Small… Electrophysiology StudyAn electrophysiology study is performed to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart.
The purpose of the…
Electrophysiology StudyAn electrophysiology study is performed to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart.
The purpose of the… Exercise Stress TestAn exercise stress test is a diagnostic test in which a person walks on a treadmill or pedals a stationary bicycle…
Exercise Stress TestAn exercise stress test is a diagnostic test in which a person walks on a treadmill or pedals a stationary bicycle… External DefibrillatorAn external defibrillator is a machine that is used to deliver an electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal…
External DefibrillatorAn external defibrillator is a machine that is used to deliver an electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal… Atrial Tachycardia - FocalFocal atrial tachycardia is an abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia, that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…
Atrial Tachycardia - FocalFocal atrial tachycardia is an abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia, that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical… Ventricular Tachycardia FocalFocal ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…
Ventricular Tachycardia FocalFocal ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical… Heart and LungsThe heart can be thought of as the main pump within the circulatory system. The right side of the heart collects blood…
Heart and LungsThe heart can be thought of as the main pump within the circulatory system. The right side of the heart collects blood… Heart AttackA heart attack, also referred to as a “myocardial infarction or MI”, occurs when the flow of blood and oxygen to an…
Heart AttackA heart attack, also referred to as a “myocardial infarction or MI”, occurs when the flow of blood and oxygen to an… Heart BlockHeart block is an arrhythmia (or “abnormal heart rhythm) in which electrical signals traveling from the atria to the…
Heart BlockHeart block is an arrhythmia (or “abnormal heart rhythm) in which electrical signals traveling from the atria to the… Heart FailureHeart failure is the term used to describe many conditions of the heart that lead to symptoms such as breathlessness,…
Heart FailureHeart failure is the term used to describe many conditions of the heart that lead to symptoms such as breathlessness,… Heart LocationThe heart is located within the rib cage, under and slightly to the left of the breastbone (sternum). It approximately…
Heart LocationThe heart is located within the rib cage, under and slightly to the left of the breastbone (sternum). It approximately… Heart TransplantA heart transplant is a surgical procedure that replaces a failing heart with a healthy donor heart. Physicians make a…
Heart TransplantA heart transplant is a surgical procedure that replaces a failing heart with a healthy donor heart. Physicians make a… Heart Valve DiseaseValvular heart disease is any condition that disrupts the proper function of the valve. There are four valves in the…
Heart Valve DiseaseValvular heart disease is any condition that disrupts the proper function of the valve. There are four valves in the… Heart Valve SurgeryHeart valve replacement surgery replaces an abnormal or diseased heart valve with a healthy one. The replacement valve…
Heart Valve SurgeryHeart valve replacement surgery replaces an abnormal or diseased heart valve with a healthy one. The replacement valve… High Blood PresureHigh blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition in which blood pressure levels are measured above the normal…
High Blood PresureHigh blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition in which blood pressure levels are measured above the normal… HBP ComplicationsBlood pressure is a measurement that reflects the pressure within the arteries. When the heart pumps, the higher…
HBP ComplicationsBlood pressure is a measurement that reflects the pressure within the arteries. When the heart pumps, the higher… High CholesterolCholesterol is a fatty type substance produced by the body and absorbed from the food you eat. Some cholesterol is…
High CholesterolCholesterol is a fatty type substance produced by the body and absorbed from the food you eat. Some cholesterol is… Holter MonitorA Holter monitor is a battery-operated, portable device that measures and tape-records your heart’s electrical activity…
Holter MonitorA Holter monitor is a battery-operated, portable device that measures and tape-records your heart’s electrical activity… Cardiomyopathy HypertrophicHypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle in which the wall of the heart, particularly the muscular…
Cardiomyopathy HypertrophicHypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle in which the wall of the heart, particularly the muscular… Ventric. Tachy. IdiopathicIdiopathic ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…
Ventric. Tachy. IdiopathicIdiopathic ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical… ICD DeviceAn implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a battery-powered device placed under your skin, beneath the…
ICD DeviceAn implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a battery-powered device placed under your skin, beneath the… Loop RecorderAn implantable loop recorder is a small device that is implanted under the skin to help identify the causes of…
Loop RecorderAn implantable loop recorder is a small device that is implanted under the skin to help identify the causes of… Ventric. Tach. Ischem. TachycardiaIschemic Ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical…
Ventric. Tach. Ischem. TachycardiaIschemic Ventricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical… LeadA lead is a device that allows the passage of electrical signals. Leads are used in electrocardiograms to record the…
LeadA lead is a device that allows the passage of electrical signals. Leads are used in electrocardiograms to record the… Long QT SyndromeLong QT Syndrome is a condition that is characterized by a delay in repolarization of the heart after the initial…
Long QT SyndromeLong QT Syndrome is a condition that is characterized by a delay in repolarization of the heart after the initial… Mitral ValveThe mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. It allows blood to flow from the…
Mitral ValveThe mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. It allows blood to flow from the… Mitral StenosisThe mitral valve is the heart valve located between the left atrium (top chamber) and left ventricle (bottom chamber…
Mitral StenosisThe mitral valve is the heart valve located between the left atrium (top chamber) and left ventricle (bottom chamber… PacemakersA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or…
PacemakersA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or… Pacemakers - DualA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or…
Pacemakers - DualA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or… Passive Fixation LeadA passive fixation lead is a type of pacemaker or defibrillator “wire” that is used to send the electrical signal of…
Passive Fixation LeadA passive fixation lead is a type of pacemaker or defibrillator “wire” that is used to send the electrical signal of… Patent Foramen OvalePatent Foramen Ovale, or PFO, is a hole in the septum that separates the upper chambers of the heart. This hole is…
Patent Foramen OvalePatent Foramen Ovale, or PFO, is a hole in the septum that separates the upper chambers of the heart. This hole is… PVCPremature ventricular contraction (PVC) is an abnormal heartbeat in which the ventricle contracts early without…
PVCPremature ventricular contraction (PVC) is an abnormal heartbeat in which the ventricle contracts early without… Pulmonary EmbolismA pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that had “traveled” to the lungs, most commonly from blood clots in the legs. The…
Pulmonary EmbolismA pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that had “traveled” to the lungs, most commonly from blood clots in the legs. The… Right AtriumThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria, and are separated into the right and…
Right AtriumThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are the atria, and are separated into the right and… Ventric. Tach. RVOT.Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Ventricular Tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal…
Ventric. Tach. RVOT.Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Ventricular Tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal… Single VentricleSingle ventricle is a birth defect in which one lower chamber (ventricle) of the heart is abnormally small…
Single VentricleSingle ventricle is a birth defect in which one lower chamber (ventricle) of the heart is abnormally small… Sinus BradycardiaSinus bradycardia is a condition in which the heart beats too slowly (less than 60 beats per minute). It may be caused…
Sinus BradycardiaSinus bradycardia is a condition in which the heart beats too slowly (less than 60 beats per minute). It may be caused… Sinus RhythmSinus rhythm is referred to as the “normal” heart rhythm. It represents the pattern of electrical activity that is seen…
Sinus RhythmSinus rhythm is referred to as the “normal” heart rhythm. It represents the pattern of electrical activity that is seen… Sinus TachycardiaSinus tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat that is caused by a sino-atrial node that fires too rapidly.
The electrical…
Sinus TachycardiaSinus tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat that is caused by a sino-atrial node that fires too rapidly.
The electrical… Smoking CessationSmoking cessation refers to quitting smoking. Quitting smoking is not easy, but there are things you can do to increase…
Smoking CessationSmoking cessation refers to quitting smoking. Quitting smoking is not easy, but there are things you can do to increase… StrokeStroke results from the sudden loss of blood flow to the brain, usually a specific part of the brain. The brain needs a…
StrokeStroke results from the sudden loss of blood flow to the brain, usually a specific part of the brain. The brain needs a… SVTThe electrical system of the heart is made up of several parts that communicate with one another to signal the heart…
SVTThe electrical system of the heart is made up of several parts that communicate with one another to signal the heart… SyncopeSyncope (or fainting) is a temporary loss of consciousness, with the inability to maintain postural tone. When patients…
SyncopeSyncope (or fainting) is a temporary loss of consciousness, with the inability to maintain postural tone. When patients… Ventric. Assist DeviceA ventricular assist device is a pumping device that is used to help a heart that can no longer pump blood effectively…
Ventric. Assist DeviceA ventricular assist device is a pumping device that is used to help a heart that can no longer pump blood effectively… Ventric. FibrillationVentricular fibrillation is a very fast, irregular heartbeat that is caused by abnormal firing of electrical signals in…
Ventric. FibrillationVentricular fibrillation is a very fast, irregular heartbeat that is caused by abnormal firing of electrical signals in… Ventric. Septal DefectVentricular septal defect, or VSD, is a hole in the wall or septum that separates the right and left lower chambers…
Ventric. Septal DefectVentricular septal defect, or VSD, is a hole in the wall or septum that separates the right and left lower chambers… Ventric. TachycardiaVentricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical signals in…
Ventric. TachycardiaVentricular tachycardia is an abnormally rapid heartbeat that is caused by an abnormal firing of electrical signals in… Ventric. Tach. AblationVentricular tachycardia ablation is a procedure used to correct ventricular tachycardia by destroying the tissue that…
Ventric. Tach. AblationVentricular tachycardia ablation is a procedure used to correct ventricular tachycardia by destroying the tissue that… Wolff-Parkinson WhiteWolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) is a condition in which the heart beats too fast due to abnormal, extra electrical…
Wolff-Parkinson WhiteWolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) is a condition in which the heart beats too fast due to abnormal, extra electrical…