Asprin
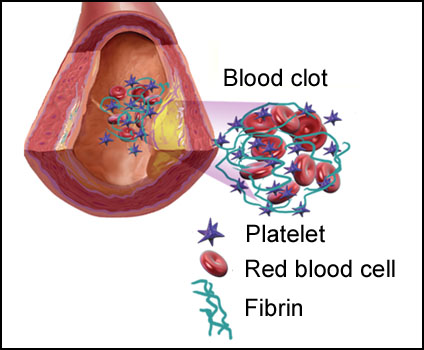
Aspirin has been shown to help prevent heart attack and stroke. Aspirin works by affecting the blood clotting process. Normally, a chain reaction started by a trigger event that leads to blood clot formation. Aspirin affects the step where platelets in the blood become sticky, resulting in less clotting.
The American Heart Association recommends aspirin use for those who’ve had a heart attack (myocardial infarction), unstable angina, ischemic stroke (caused by blood clot) or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), if not contraindicated. Studies show aspirin also helps prevent these events from occurring in people who are at high risk for heart disease, heart attack and stroke. Aspirin has been proven to help prevent the recurrence of such events as heart attack, as well as hospitalization for recurrent angina and second strokes.
Figure 1: Aspirin
Figure 2: Components of a blood clot.
Figure 3: Normal clotting chain reaction in the blood.
Figure 4: Aspirin affects the blood clotting reaction and reduces blood clotting.
Visit Ohio Heart and Vascular Center for more information.