Wolff-Parkinson White Syndrome
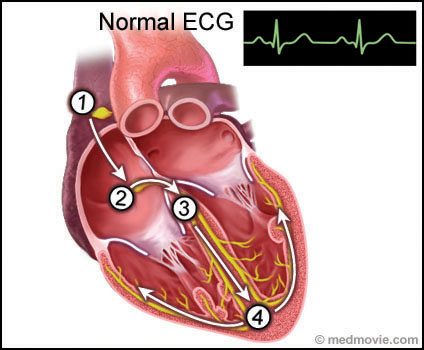
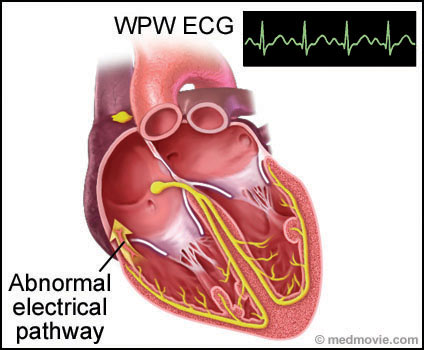
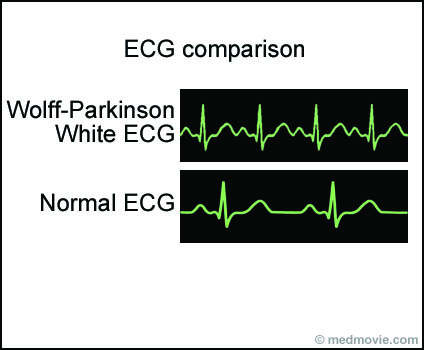
Wolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) is a condition in which the heart beats too fast due to abnormal, extra electrical pathways between the heart’s upper and lower chambers. In a normal heart, the electrical signal moves from the heart’s upper chambers (the atria) to the lower chambers (the ventricles), causing the heart to beat. If there’s an extra conduction pathway, the electrical signal may cause a rapid heart rate (tachycardia). WPW can be present at birth (congenital), but symptoms can appear at any time. More women than men are diagnosed with WPW. Treatments include medications and some surgical procedures.
cvml_0266i
Visit Medmovie.com Website for more information.