

Atrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disorder. In atrial fibrillation, abnormal signals from the left atrium completely disrupt the normal rhythm, which becomes irregular and fast. Most often these abnormal signals come from the pulmonary veins. Under these conditions, the heart contracts in a disordered manner and does not pump blood efficiently.
To stop this arrhythmia, your doctor may suggest cardioversion. The procedure typically lasts about 15 minutes, uses sedation, and often requires an outpatient hospital stay. Your doctor will either monitor your anticoagulation medications prior to the procedure or may perform a transesophageal echocardiogram to check for blood clots.
ECG electrodes monitor the heart’s electrical activity. Two pads or paddles will be placed on the skin of the chest or the chest and back. These pads or paddles will deliver an electrical shock to your heart. This may be repeated several times until normal electrical activity resumes.
Cardioversion is a straightforward procedure when performed by experienced healthcare providers. Ask your doctor or your cardiologist for further details.
©2024 Medmovie.com. All rights reserved. Medmovie.com creates and licenses medical illustrations and animations for educational use. Our goal is to increase your understanding of medical terminology and help communication between patients, caregiver and healthcare professionals. The content in the Media Library is for your information and education purposes only. The Media Library is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment for specific medical conditions.
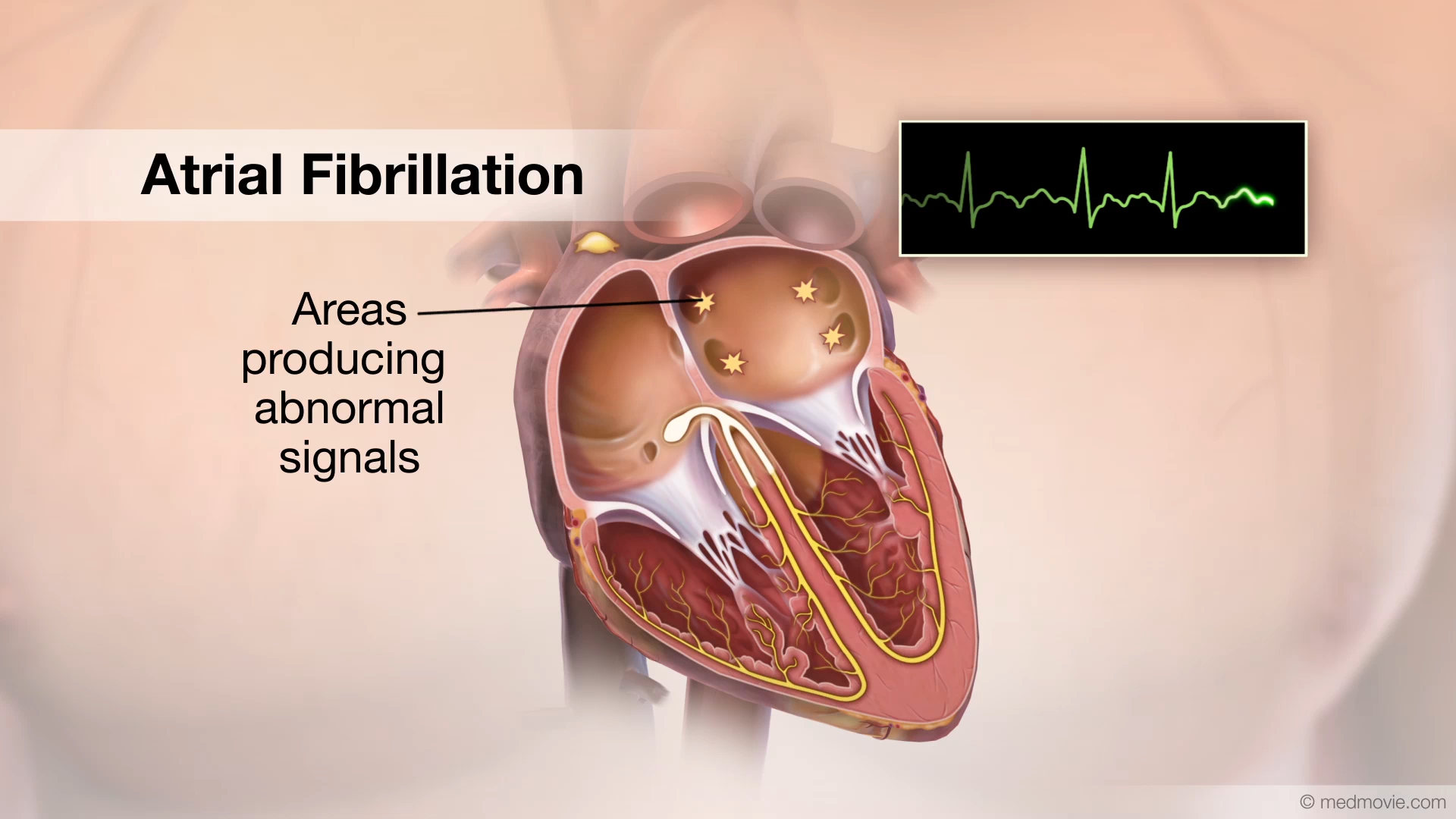 Atrial FibrillationThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
Atrial FibrillationThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell… Atrial Fibrillation AblationAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers) Atrial…
Atrial Fibrillation AblationAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers) Atrial…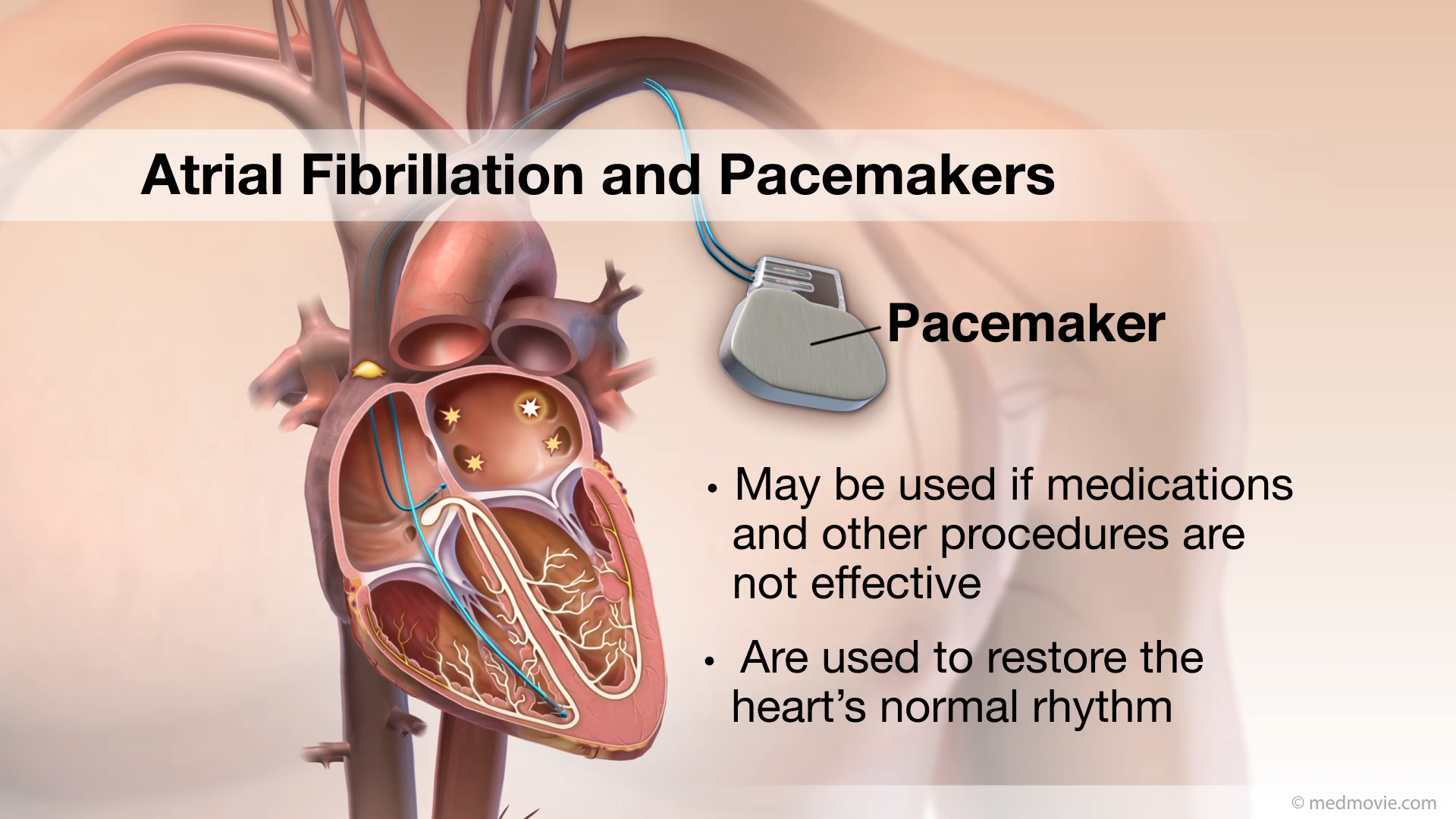 Atrial Fibrillation PacemakersAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers) of the…
Atrial Fibrillation PacemakersAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers) of the…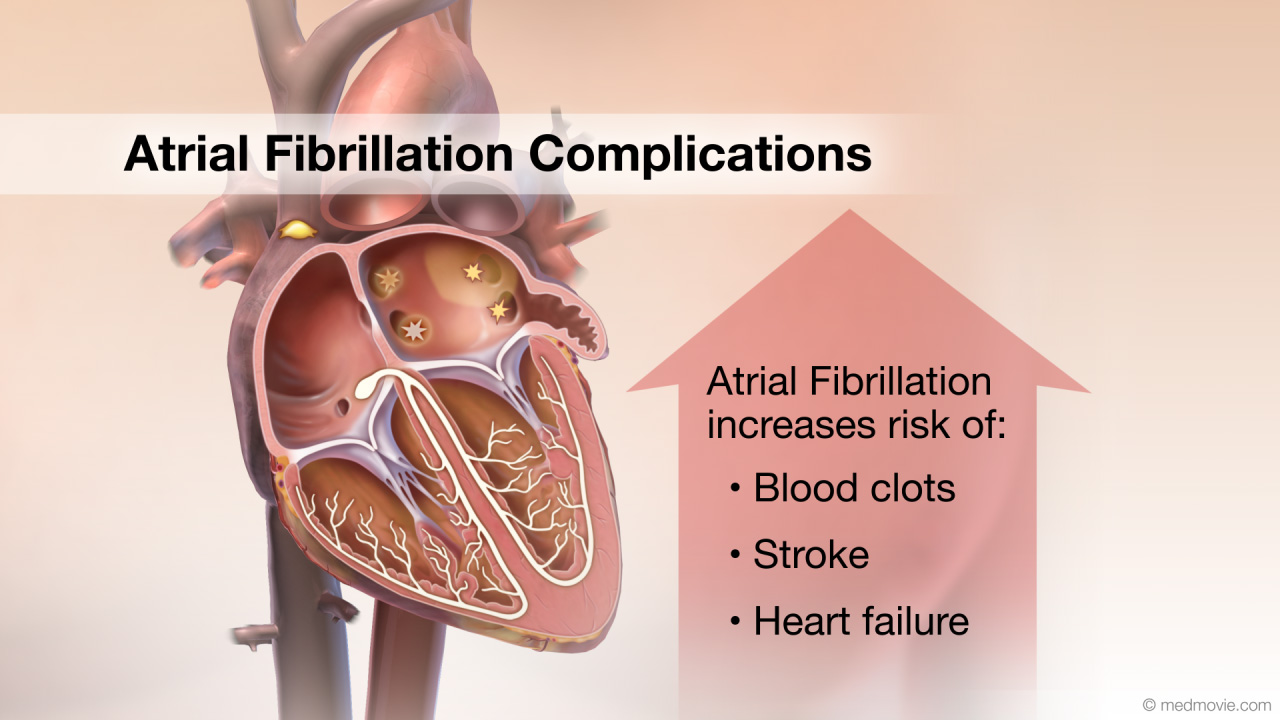 Atrial Fibrillation ComplicationsAtrial fibrillation (AF) is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers)…
Atrial Fibrillation ComplicationsAtrial fibrillation (AF) is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers)… Atrial Fibrillation MedicationsAtrial Fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (or top chambers) of…
Atrial Fibrillation MedicationsAtrial Fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (or top chambers) of…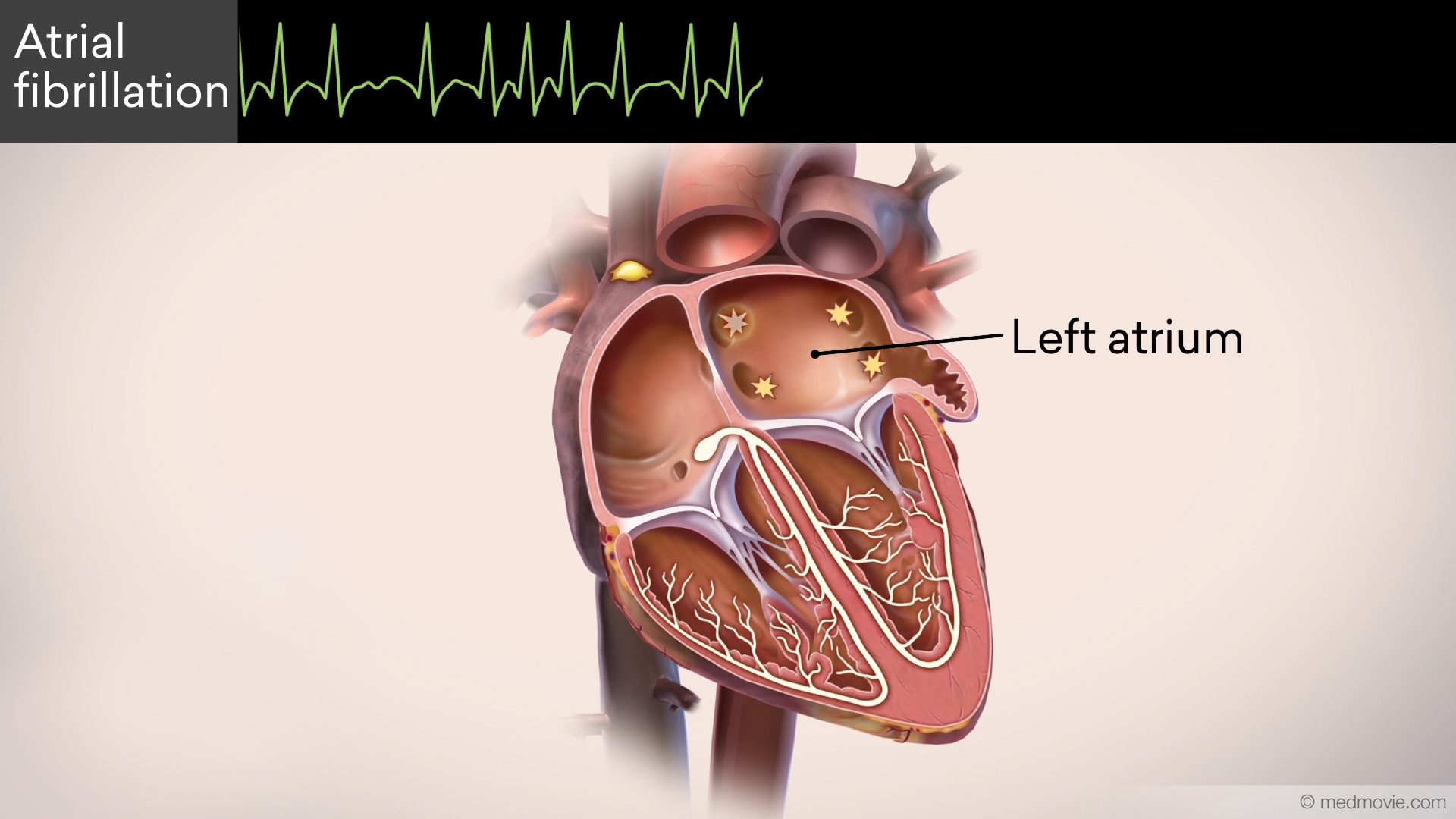 Atrial Fibrillation OverviewAtrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disorder. In atrial fibrillation, abnormal signals from the left…
Atrial Fibrillation OverviewAtrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disorder. In atrial fibrillation, abnormal signals from the left… AV Node AblationAV node ablation is a procedure used to correct irregular heartbeats by destroying the tissue within the AV node. AV…
AV Node AblationAV node ablation is a procedure used to correct irregular heartbeats by destroying the tissue within the AV node. AV…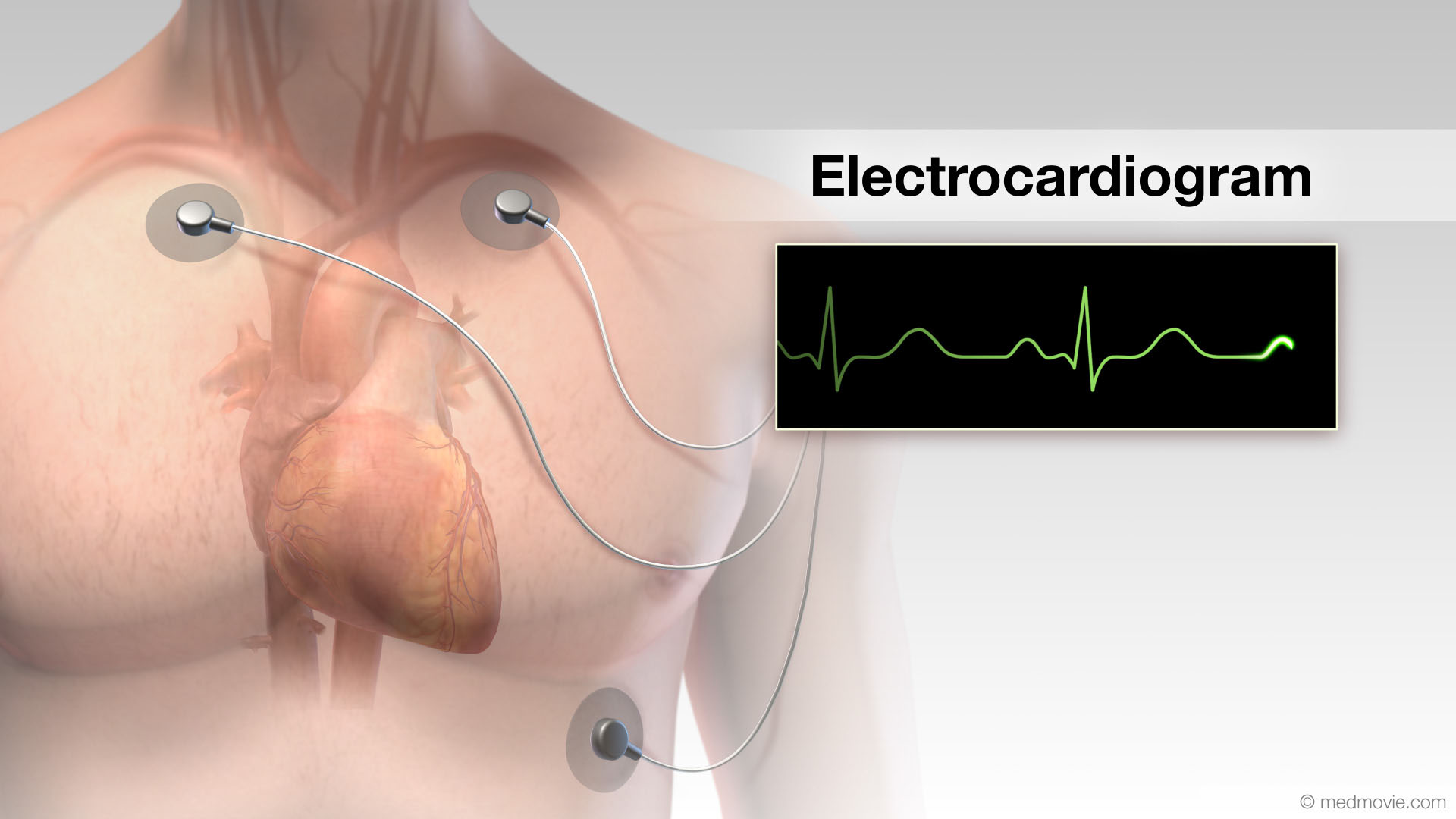 ElectrocardiogramThe electrocardiogram or ECG, records the electrical activity of the heart. It is used to determine if the heart has an…
ElectrocardiogramThe electrocardiogram or ECG, records the electrical activity of the heart. It is used to determine if the heart has an… ICD DeviceAn Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, or ICD, is a battery-powered device that keeps track of your heartbeat, and…
ICD DeviceAn Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, or ICD, is a battery-powered device that keeps track of your heartbeat, and… ICD OverviewAn Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, or ICD, is a battery-powered device that keeps track of your heartbeat and…
ICD OverviewAn Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, or ICD, is a battery-powered device that keeps track of your heartbeat and… Sudden Cardiac ArrestSudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is an event caused by a problem with the heart's "electrical" system. SCA occurs when the…
Sudden Cardiac ArrestSudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is an event caused by a problem with the heart's "electrical" system. SCA occurs when the…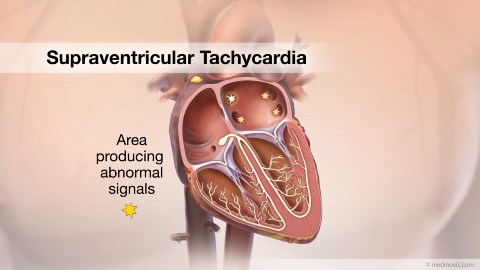 SVTThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
SVTThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…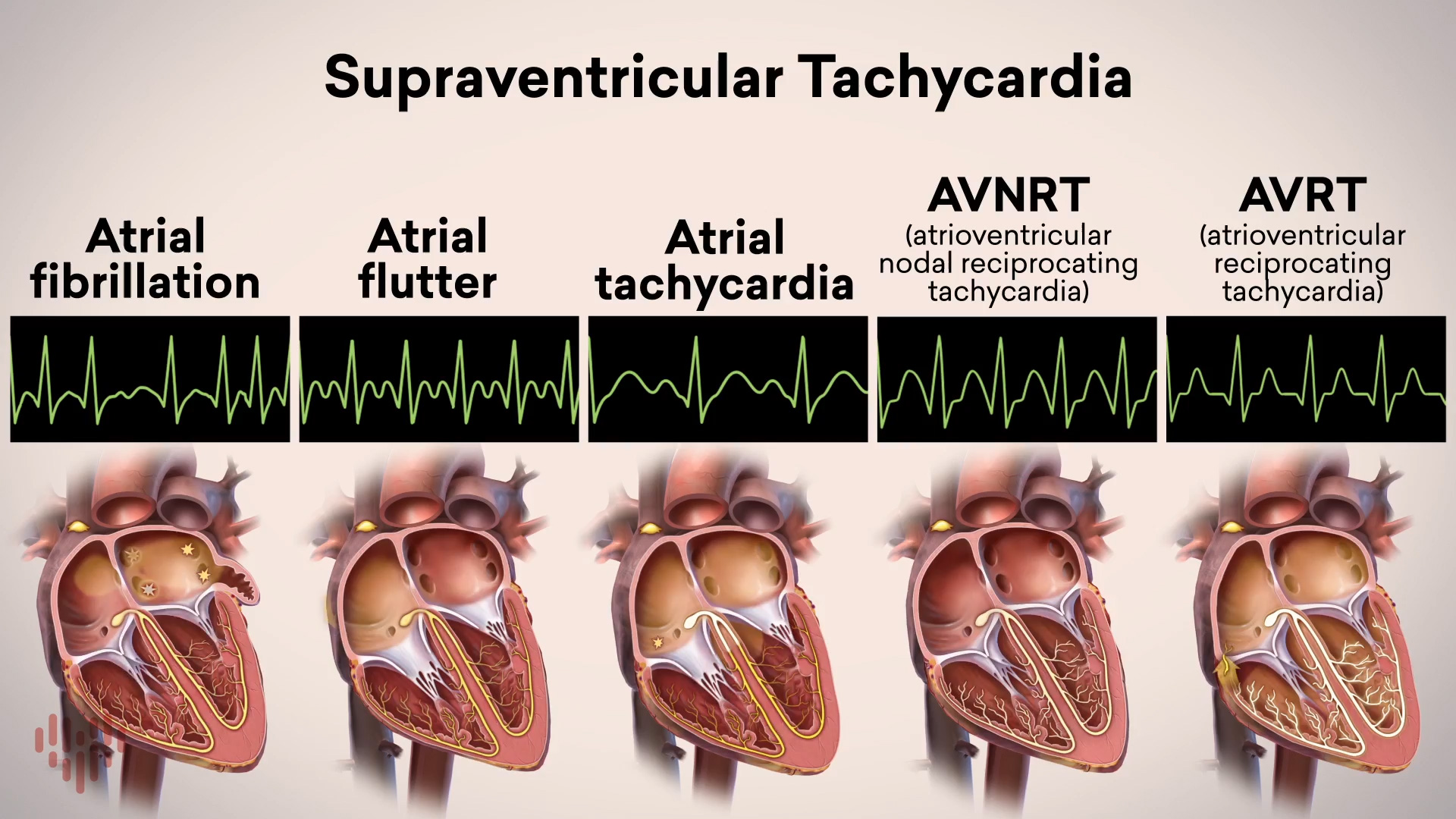 Supraventricular Tachycardia OverviewSupraventricular tachycardias are heart conditions with a fast heart rhythm and an electrical abnormality of the atria…
Supraventricular Tachycardia OverviewSupraventricular tachycardias are heart conditions with a fast heart rhythm and an electrical abnormality of the atria…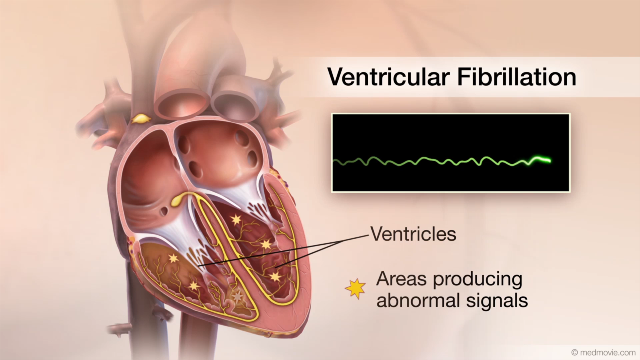 Ventricular FibrillationThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
Ventricular FibrillationThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…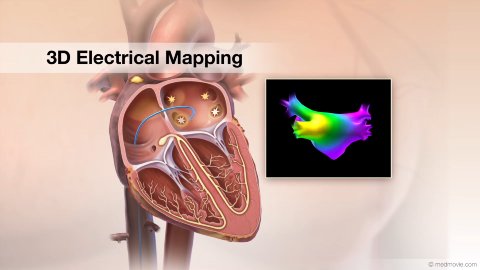 3D Electrical MappingElectrical mapping of the heart is a procedure that is used to diagnose the origins of arrhythmias. This procedure uses…
3D Electrical MappingElectrical mapping of the heart is a procedure that is used to diagnose the origins of arrhythmias. This procedure uses…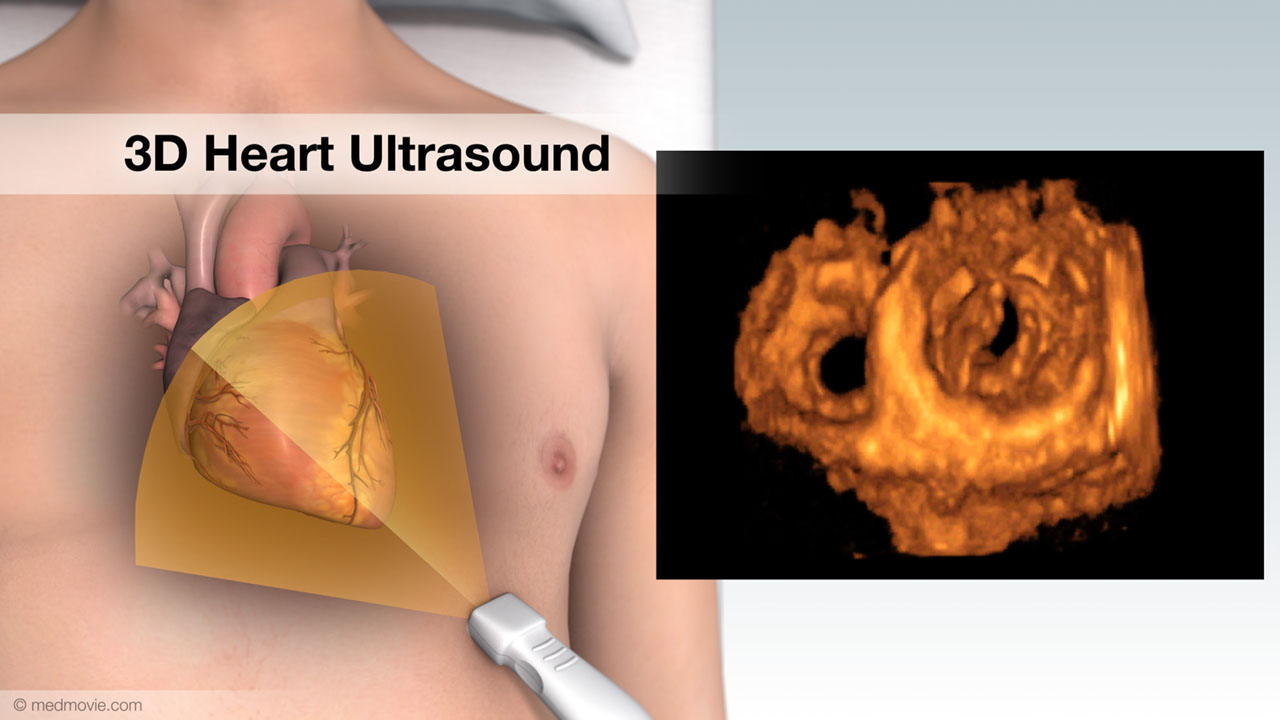 3D Heart UltrasoundA 3D heart ultrasound, also known as a 3D echocardiogram, is a diagnostic test that creates 3D videos of the heart.…
3D Heart UltrasoundA 3D heart ultrasound, also known as a 3D echocardiogram, is a diagnostic test that creates 3D videos of the heart.…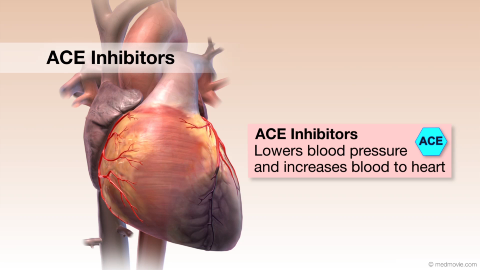 ACE InhibitorsACE Inhibitors (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme) Inhibitors are drugs used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure…
ACE InhibitorsACE Inhibitors (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme) Inhibitors are drugs used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure…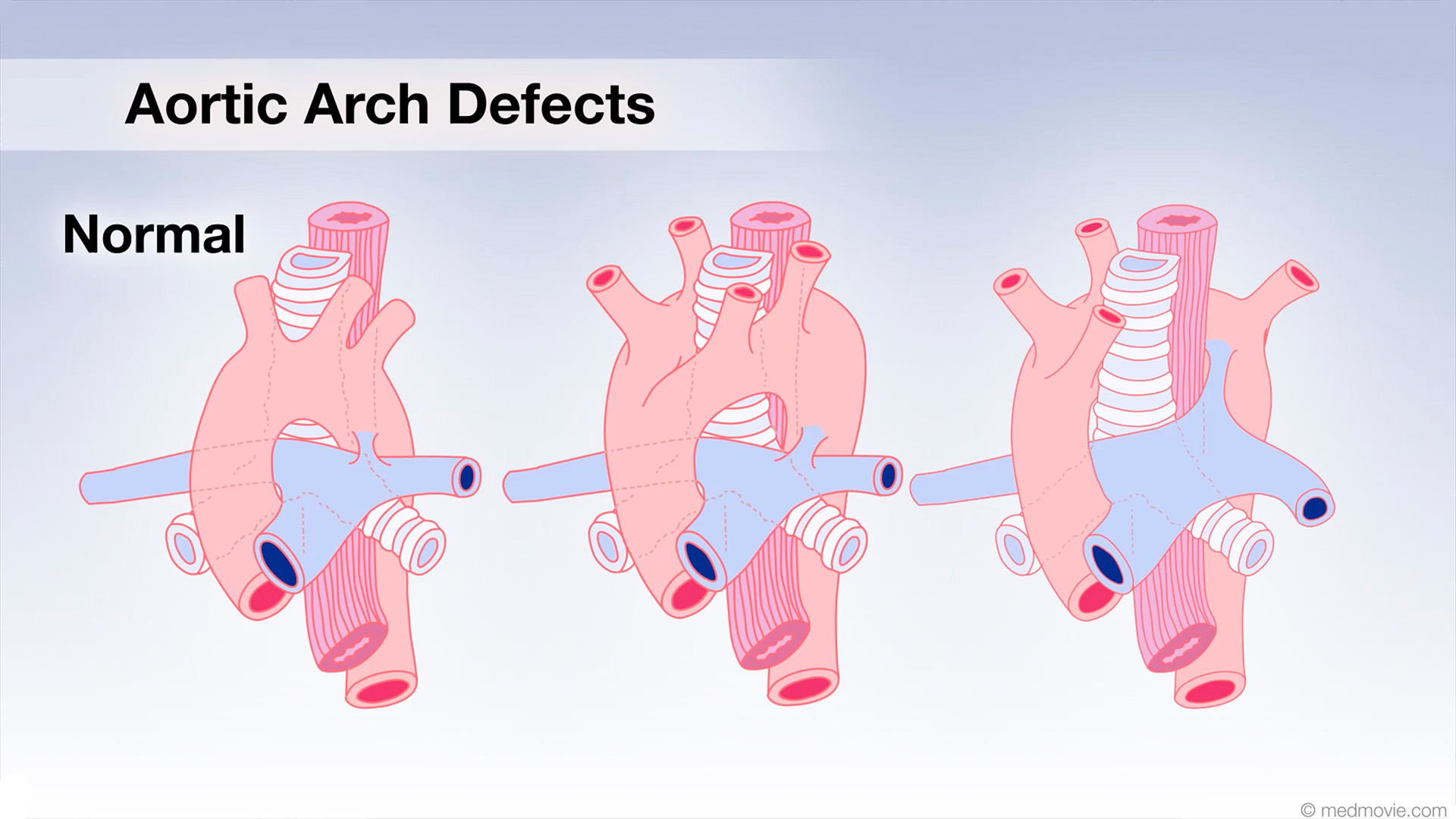 Aortic Arch DefectsIn the early stages of fetal development, two aortic arches come from the heart, ascend upward and then descend behind…
Aortic Arch DefectsIn the early stages of fetal development, two aortic arches come from the heart, ascend upward and then descend behind…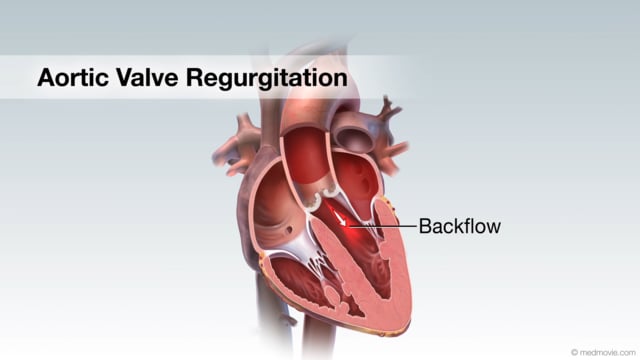 Aortic Valve RegurgitationAortic valve regurgitation results when the aortic valve, which sits between the left ventricle and the aorta, cannot…
Aortic Valve RegurgitationAortic valve regurgitation results when the aortic valve, which sits between the left ventricle and the aorta, cannot… Aortic Valve StenosisThe aortic valve is located between your heart’s main pumping chamber (left ventricle) and the major artery (aorta)…
Aortic Valve StenosisThe aortic valve is located between your heart’s main pumping chamber (left ventricle) and the major artery (aorta)…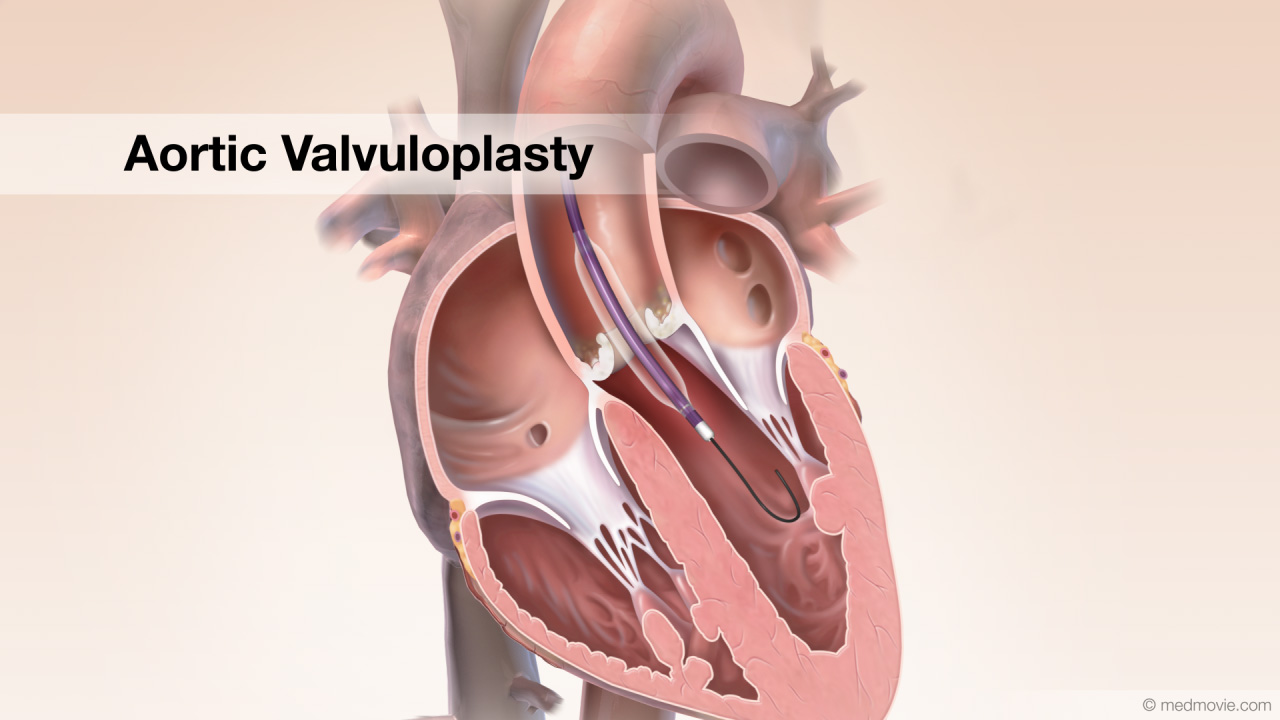 Aortic ValvuloplastyStenotic aortic valve disease can require a procedure called aortic valvuloplasty. Calcific aortic stenosis is shown…
Aortic ValvuloplastyStenotic aortic valve disease can require a procedure called aortic valvuloplasty. Calcific aortic stenosis is shown…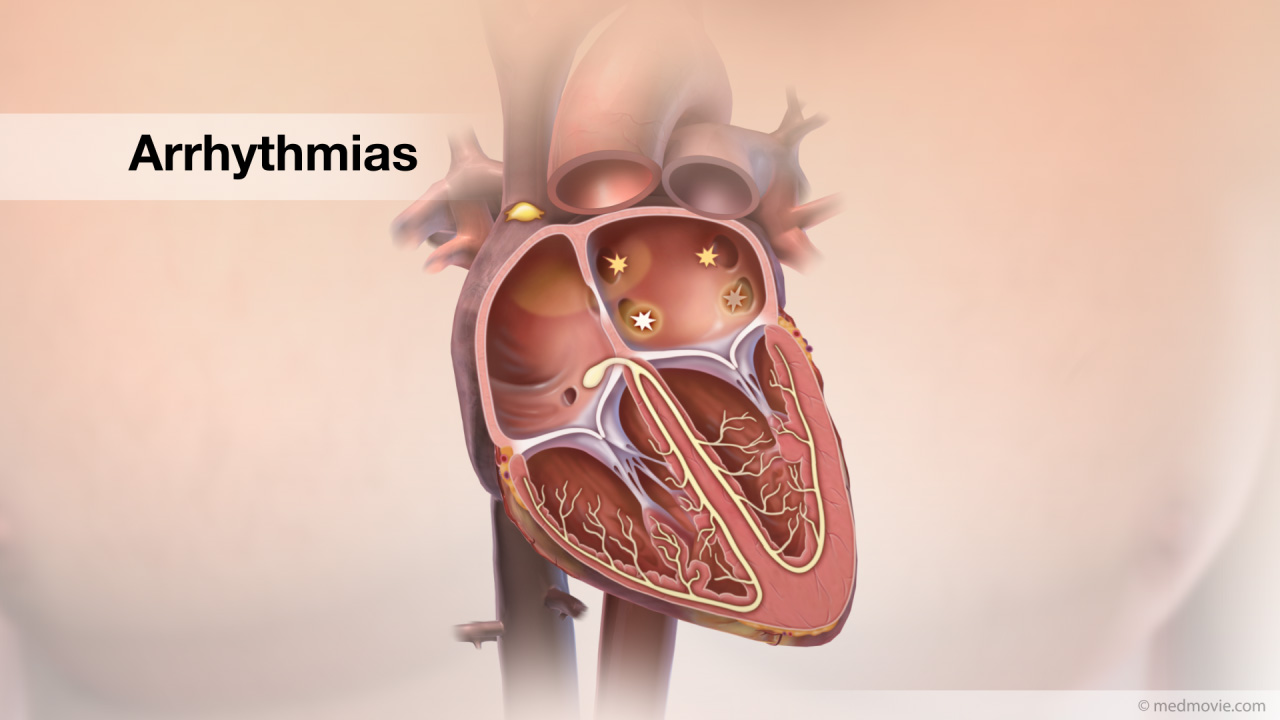 ArrhythmiasThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several sequences that…
ArrhythmiasThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several sequences that… AtherosclerosisAtherosclerosis is a disease that affects the arteries, which carry blood to the organs of the body.
Normal arteries…
AtherosclerosisAtherosclerosis is a disease that affects the arteries, which carry blood to the organs of the body.
Normal arteries… Atrial FibrillationThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
Atrial FibrillationThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell… Atrial Fibrillation AblationAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers) Atrial…
Atrial Fibrillation AblationAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers) Atrial… Atrial Fibrillation PacemakersAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers) of the…
Atrial Fibrillation PacemakersAtrial fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers) of the… Atrial Fibrillation CardioversionAtrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disorder. In atrial fibrillation, abnormal signals from the left…
Atrial Fibrillation CardioversionAtrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disorder. In atrial fibrillation, abnormal signals from the left… Atrial Fibrillation ComplicationsAtrial fibrillation (AF) is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers)…
Atrial Fibrillation ComplicationsAtrial fibrillation (AF) is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (top chambers)… Atrial Fibrillation MedicationsAtrial Fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (or top chambers) of…
Atrial Fibrillation MedicationsAtrial Fibrillation is a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal electrical signals begin in the atria (or top chambers) of… Atrial Fibrillation OverviewAtrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disorder. In atrial fibrillation, abnormal signals from the left…
Atrial Fibrillation OverviewAtrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disorder. In atrial fibrillation, abnormal signals from the left… Atrial FlutterThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made of several parts that tell the…
Atrial FlutterThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made of several parts that tell the…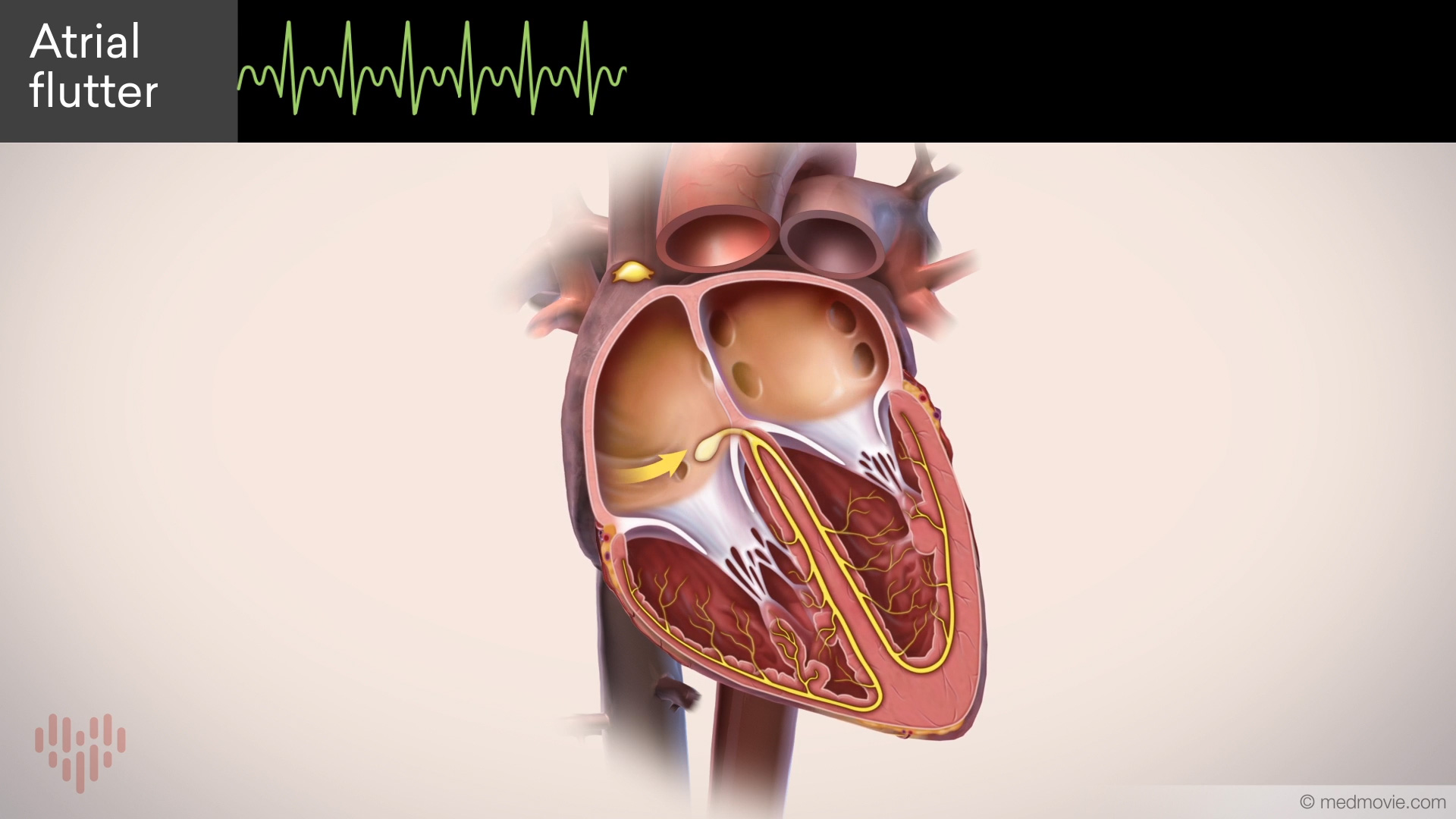 Atrial Flutter OverviewAtrial flutter is a common heart rhythm disorder. In atrial flutter, an abnormal electrical circuit spins in the right…
Atrial Flutter OverviewAtrial flutter is a common heart rhythm disorder. In atrial flutter, an abnormal electrical circuit spins in the right…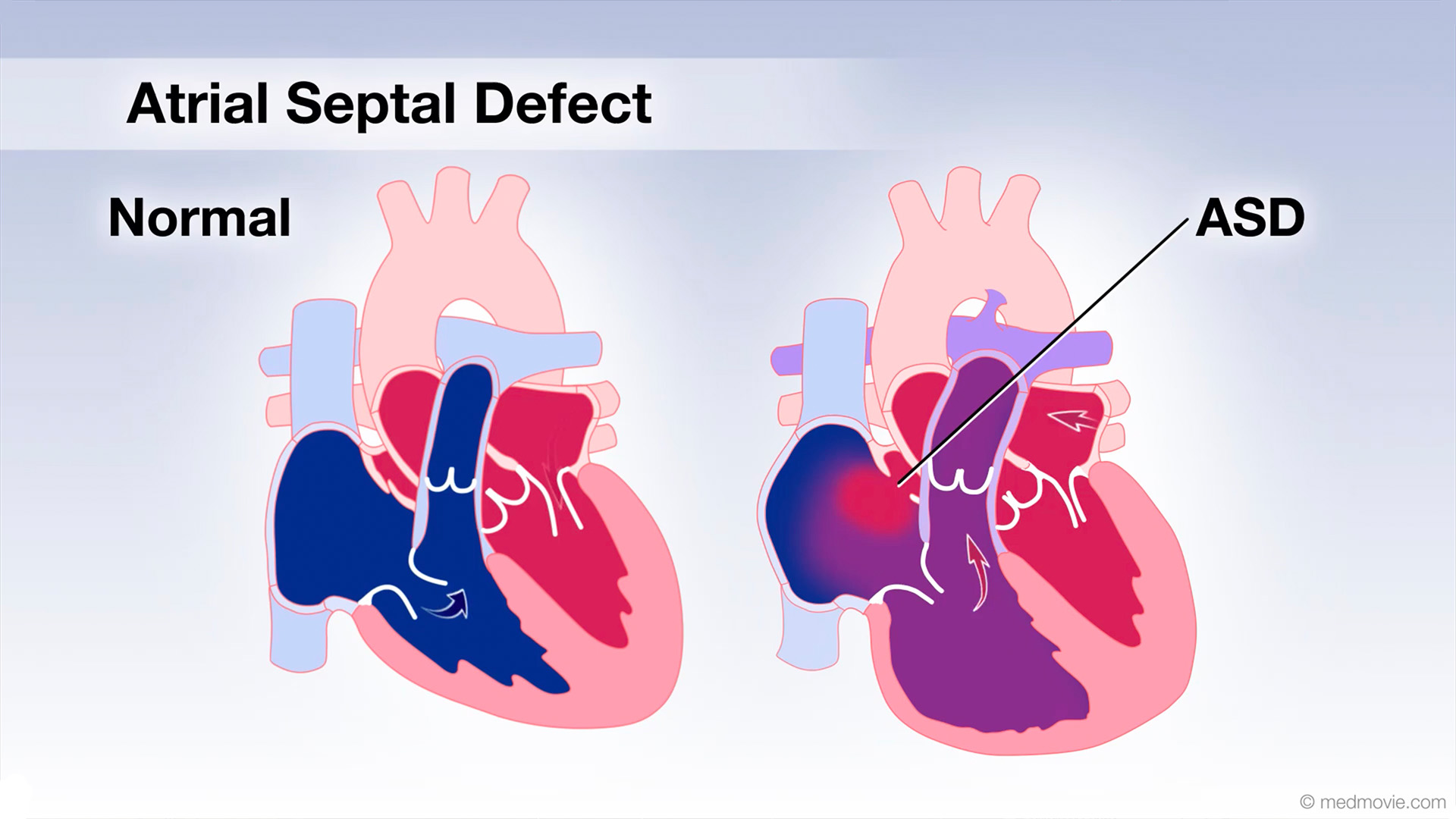 Atrial Septal DefectAn atrial septal defect, or ASD, is a hole in the wall that separates the upper two chambers of the heart, known as the…
Atrial Septal DefectAn atrial septal defect, or ASD, is a hole in the wall that separates the upper two chambers of the heart, known as the… Atrial TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
Atrial TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…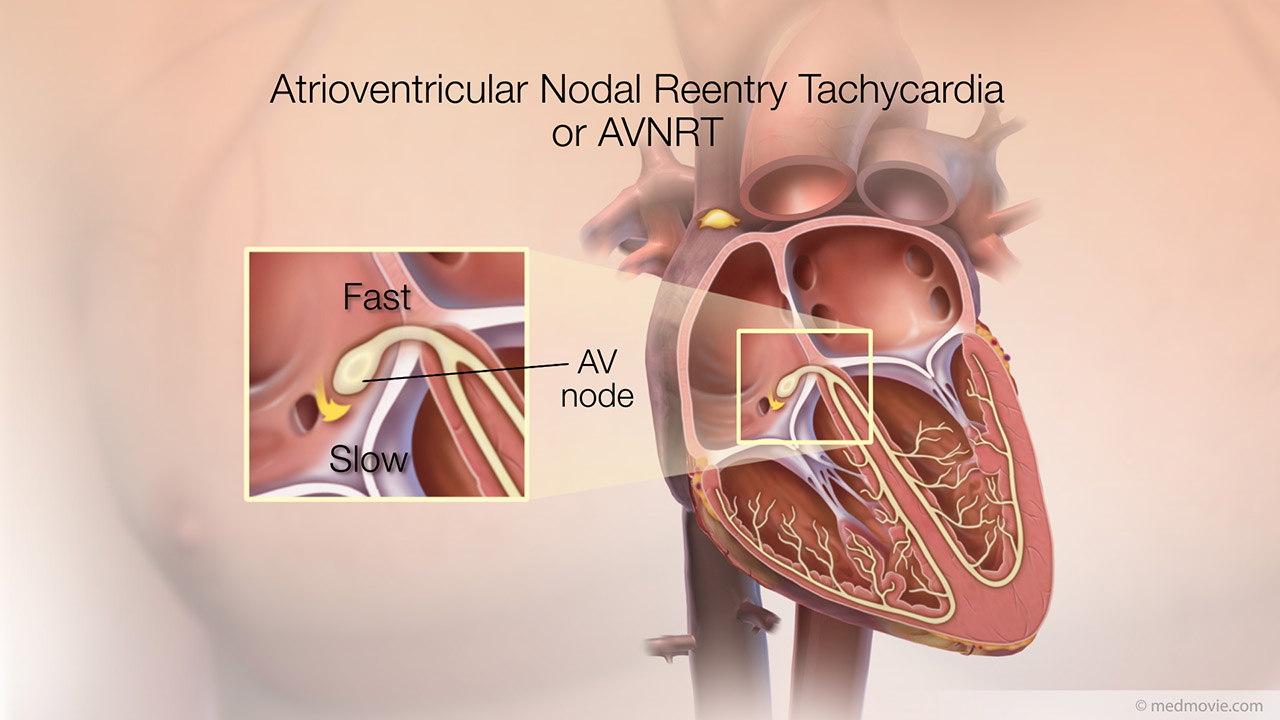 AVNRTThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
AVNRTThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell… AVRTThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
AVRTThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell… AV CanalThe atrioventricular canal, or AV canal, is the structure that forms the center of the heart. During normal fetal…
AV CanalThe atrioventricular canal, or AV canal, is the structure that forms the center of the heart. During normal fetal… AV Node AblationAV node ablation is a procedure used to correct irregular heartbeats by destroying the tissue within the AV node. AV…
AV Node AblationAV node ablation is a procedure used to correct irregular heartbeats by destroying the tissue within the AV node. AV… BradycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made of several parts that tell the…
BradycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made of several parts that tell the…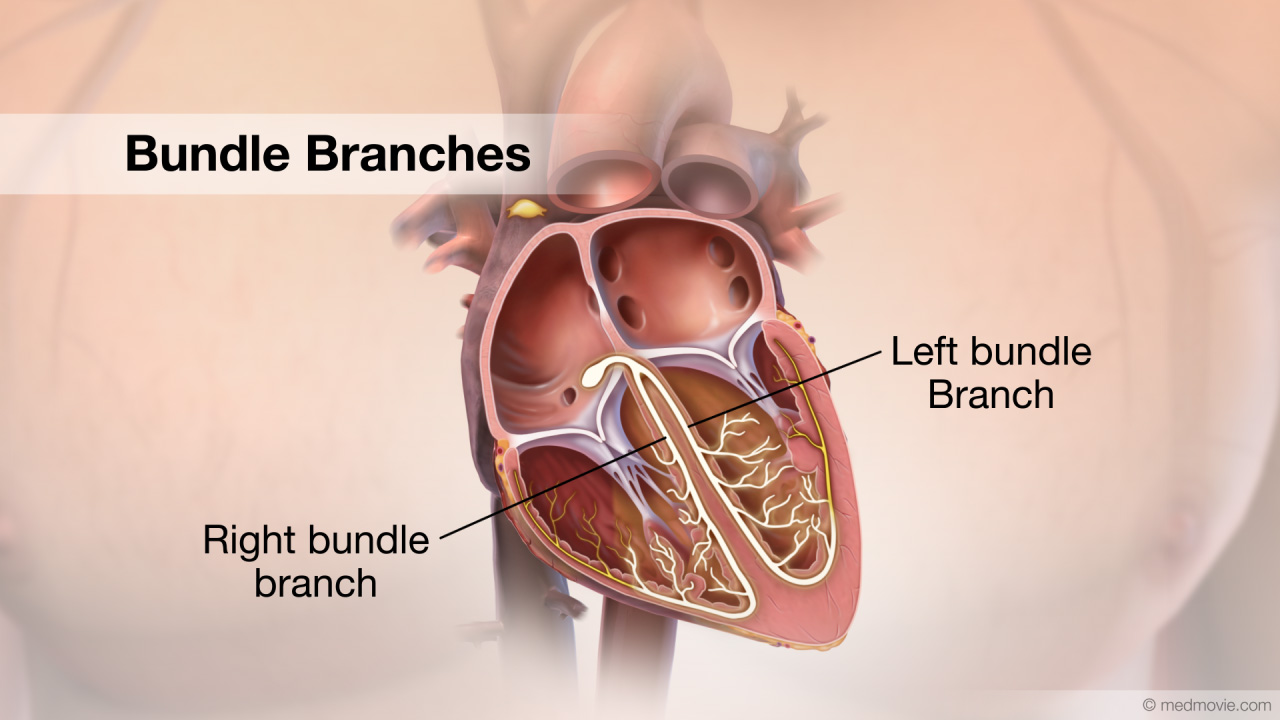 Bundle BranchesThe bundle branches are a part of the electrical system of the heart.
The electrical system controls the heartbeat…
Bundle BranchesThe bundle branches are a part of the electrical system of the heart.
The electrical system controls the heartbeat… Bundle of HisThe bundle of His is a part of the electrical system of the heart. It is a collection of cells that carry electrical…
Bundle of HisThe bundle of His is a part of the electrical system of the heart. It is a collection of cells that carry electrical… Cardiac CatheterizationCardiac catheterization refers to a procedure used to diagnose and treat certain heart conditions.
To initiate a…
Cardiac CatheterizationCardiac catheterization refers to a procedure used to diagnose and treat certain heart conditions.
To initiate a… CRT DeviceA cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your…
CRT DeviceA cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your… Catheter AblationThe electrical system of the heart controls each heartbeat. Electrical impulses generated by special tissue (nodes)…
Catheter AblationThe electrical system of the heart controls each heartbeat. Electrical impulses generated by special tissue (nodes)…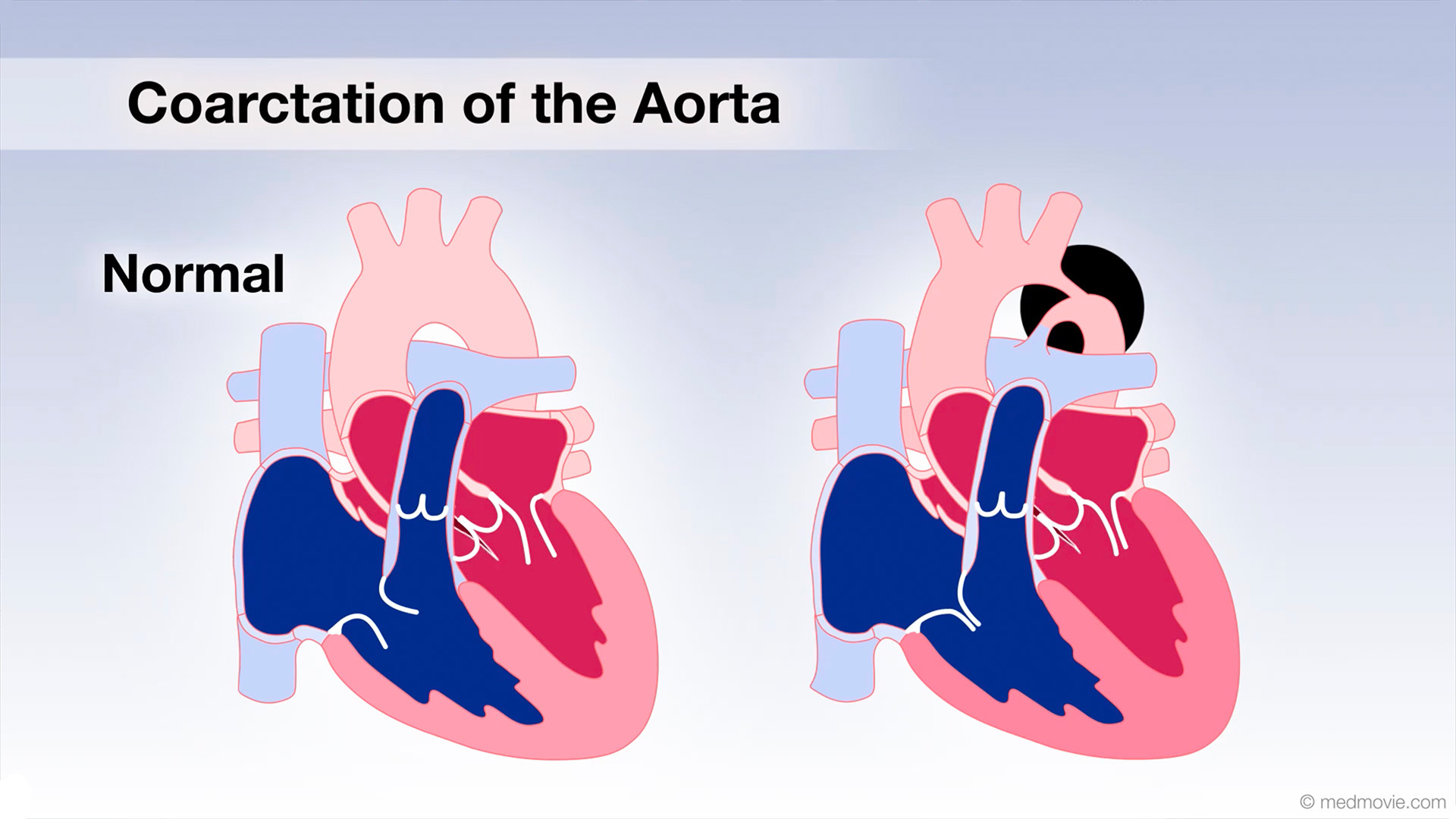 Coarctation of AortaCoarctation of the Aorta is a congenital defect in which the upper part of the descending aorta is severely narrowed or…
Coarctation of AortaCoarctation of the Aorta is a congenital defect in which the upper part of the descending aorta is severely narrowed or…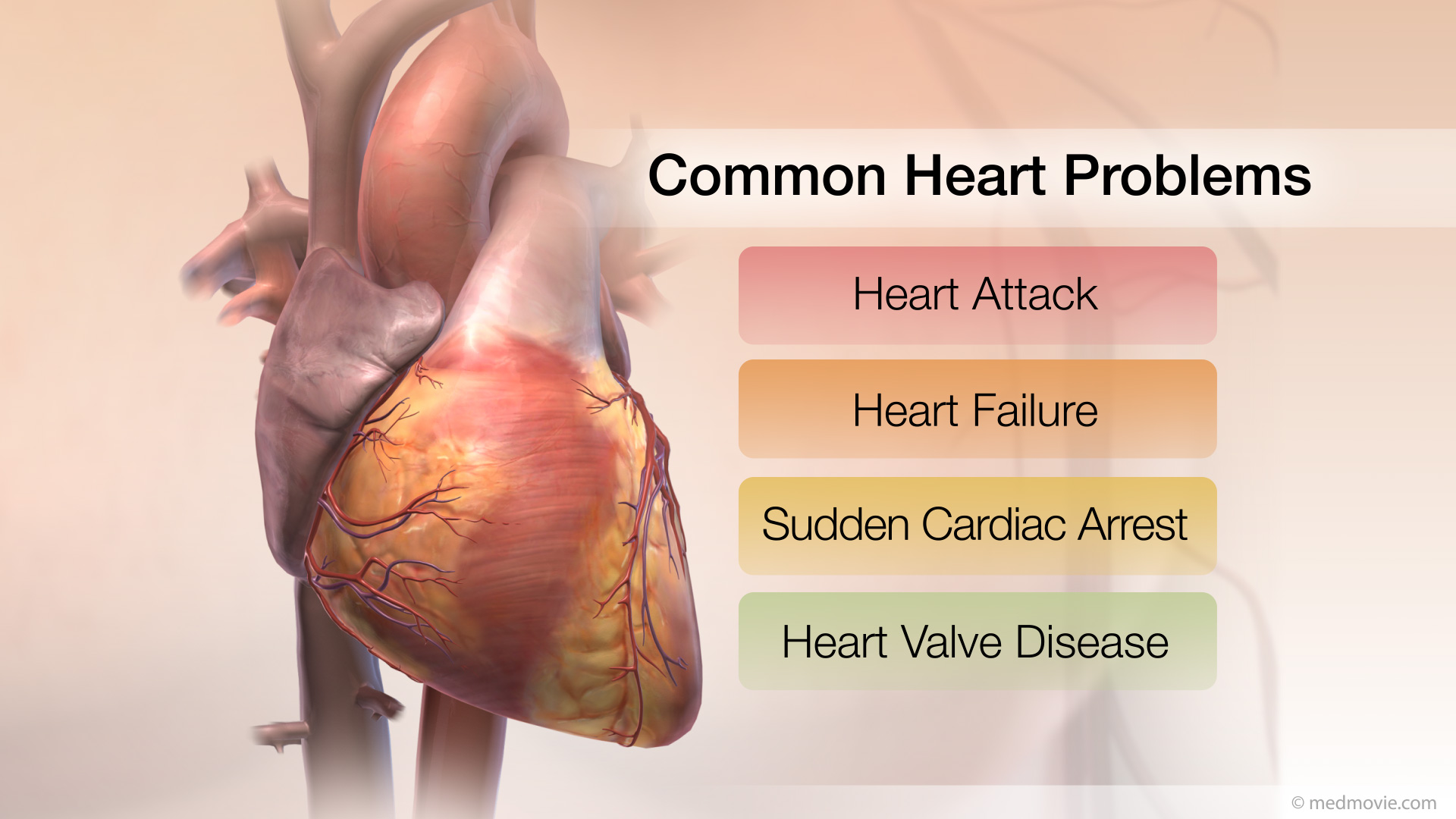 Common Heart ProblemsThe arteries, muscle, conductive tissue and valves of the heart work together to keep it beating normally. These four…
Common Heart ProblemsThe arteries, muscle, conductive tissue and valves of the heart work together to keep it beating normally. These four… Contrast EchoHeart Ultrasound provides your doctor with moving images of your heart and takes excellent pictures that will help your…
Contrast EchoHeart Ultrasound provides your doctor with moving images of your heart and takes excellent pictures that will help your… Coronary AngiogramA coronary angiogram is a test that uses x-ray imaging and contrast dye to view the coronary arteries, the blood…
Coronary AngiogramA coronary angiogram is a test that uses x-ray imaging and contrast dye to view the coronary arteries, the blood… Coronary AngioplastyCoronary angioplasty (PTCA) is a procedure that opens up narrowed or blocked segments of the arteries that supply blood…
Coronary AngioplastyCoronary angioplasty (PTCA) is a procedure that opens up narrowed or blocked segments of the arteries that supply blood… Coronary Art. DiseaseCoronary artery disease is a condition in which the coronary arteries are narrowed by deposits called plaques.
The…
Coronary Art. DiseaseCoronary artery disease is a condition in which the coronary arteries are narrowed by deposits called plaques.
The… Coronary StentA Coronary Stent is a small expandable tube shaped device used to open narrowed coronary arteries that have interrupted…
Coronary StentA Coronary Stent is a small expandable tube shaped device used to open narrowed coronary arteries that have interrupted… CRT OverviewA cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your…
CRT OverviewA cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your… CT ScanA Computed Tomography scan, or CT scan, also known as a CAT scan, is a non-invasive diagnostic test that uses x-rays to…
CT ScanA Computed Tomography scan, or CT scan, also known as a CAT scan, is a non-invasive diagnostic test that uses x-rays to… Dilated CardiomyopathyDilated cardiomyopathy is a term used to describe a condition of the heart in which one or more of the chambers of the…
Dilated CardiomyopathyDilated cardiomyopathy is a term used to describe a condition of the heart in which one or more of the chambers of the…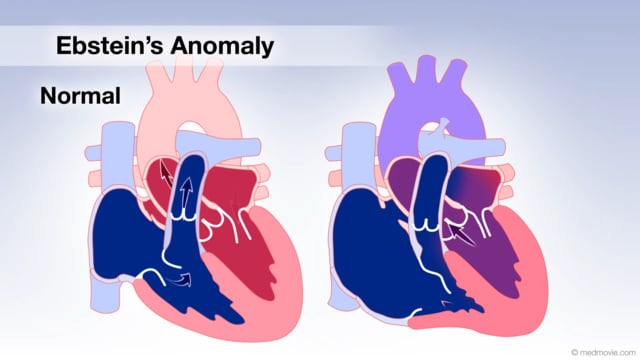 Ebstein's AnomalyThe tricuspid valve is the valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle, and in Ebstein’s anomaly it is…
Ebstein's AnomalyThe tricuspid valve is the valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle, and in Ebstein’s anomaly it is…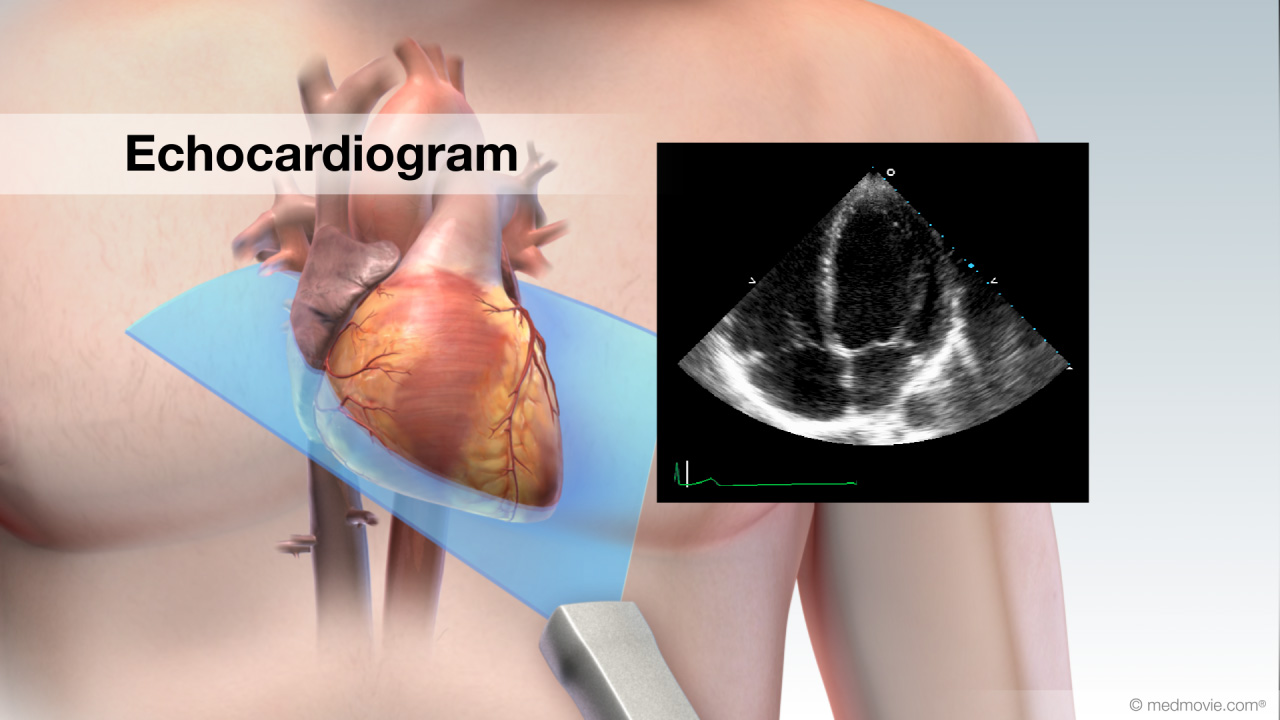 EchocardiogramAn echocardiogram, or cardiac ultrasound, is a diagnostic test that uses sound waves to view structures of the beating…
EchocardiogramAn echocardiogram, or cardiac ultrasound, is a diagnostic test that uses sound waves to view structures of the beating…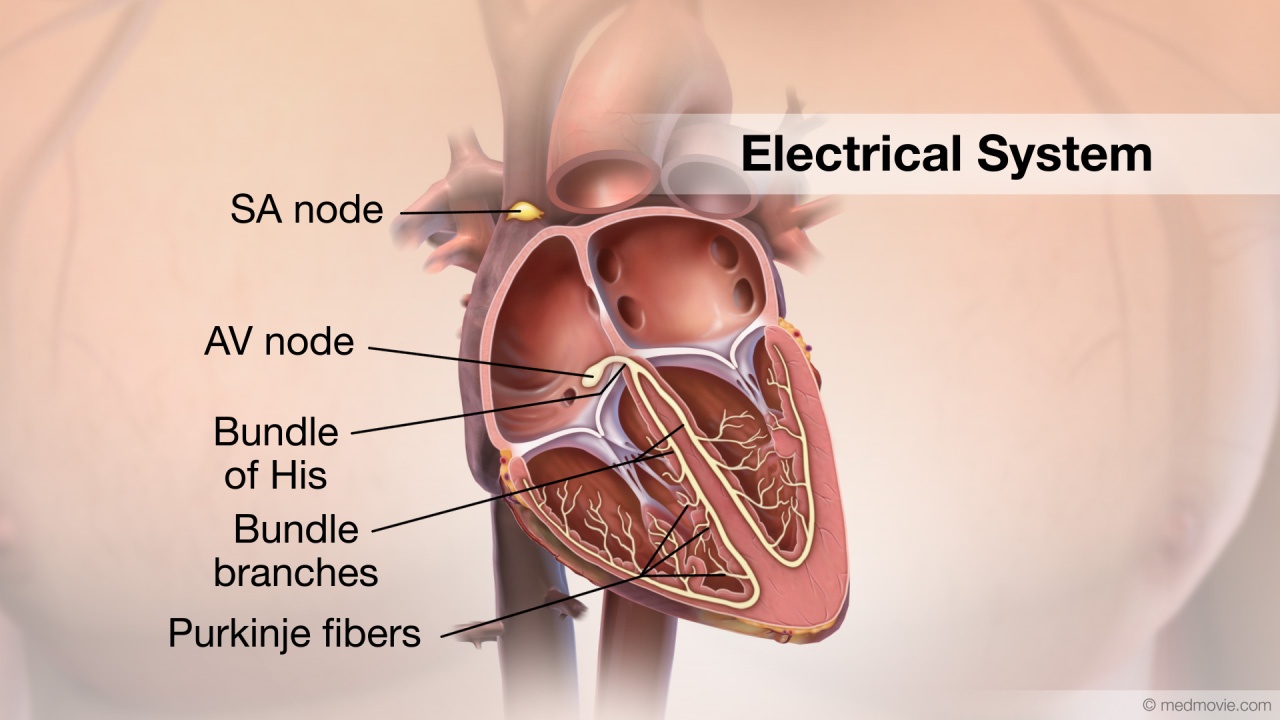 Electrical SystemThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to…
Electrical SystemThe purpose of the electrical system of the heart is to coordinate the pumping of the four chambers of the heart and to… ElectrocardiogramThe electrocardiogram or ECG, records the electrical activity of the heart. It is used to determine if the heart has an…
ElectrocardiogramThe electrocardiogram or ECG, records the electrical activity of the heart. It is used to determine if the heart has an…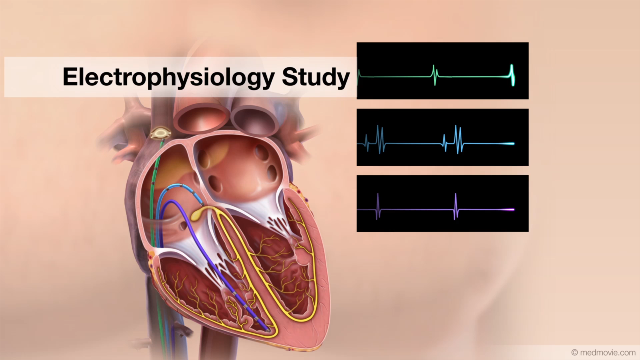 EP StudyAn electrophysiology study is performed to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart. The purpose of the electrical…
EP StudyAn electrophysiology study is performed to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart. The purpose of the electrical… Exercise Stress TestAn exercise stress test is a diagnostic test in which a person walks on a treadmill or pedals a stationary bicycle…
Exercise Stress TestAn exercise stress test is a diagnostic test in which a person walks on a treadmill or pedals a stationary bicycle… Focal Atrial TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
Focal Atrial TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell… Focal Ventricular TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
Focal Ventricular TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…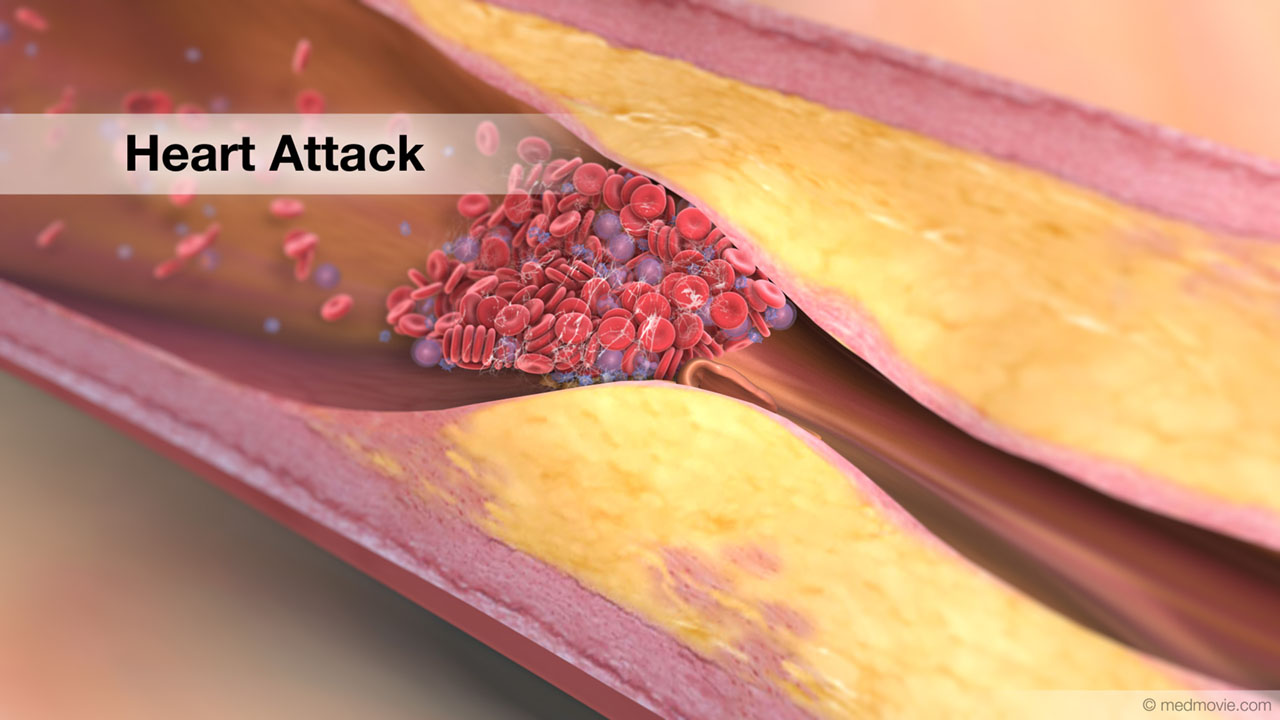 Heart AttackA heart attack happens when blood flow to an area of heart muscle suddenly becomes blocked and an area of heart muscle…
Heart AttackA heart attack happens when blood flow to an area of heart muscle suddenly becomes blocked and an area of heart muscle…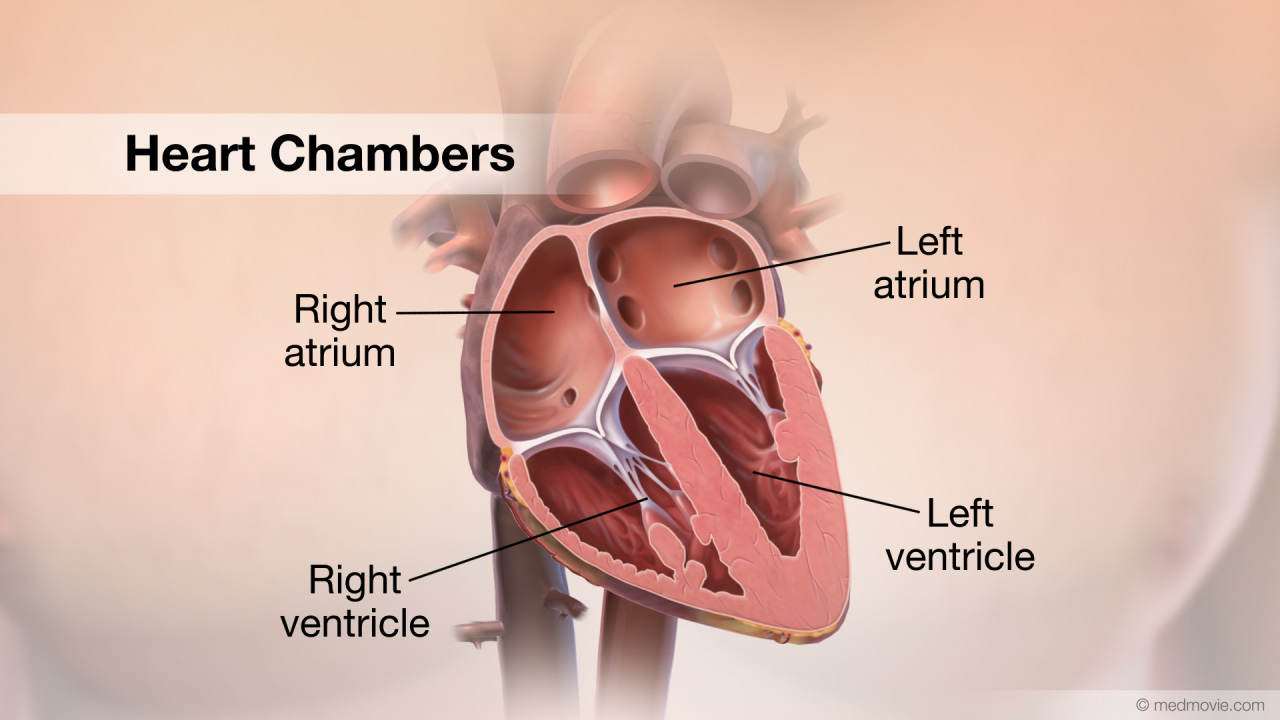 Heart ChambersThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are called the atria. The right atrium and left atrium…
Heart ChambersThe heart is divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers are called the atria. The right atrium and left atrium…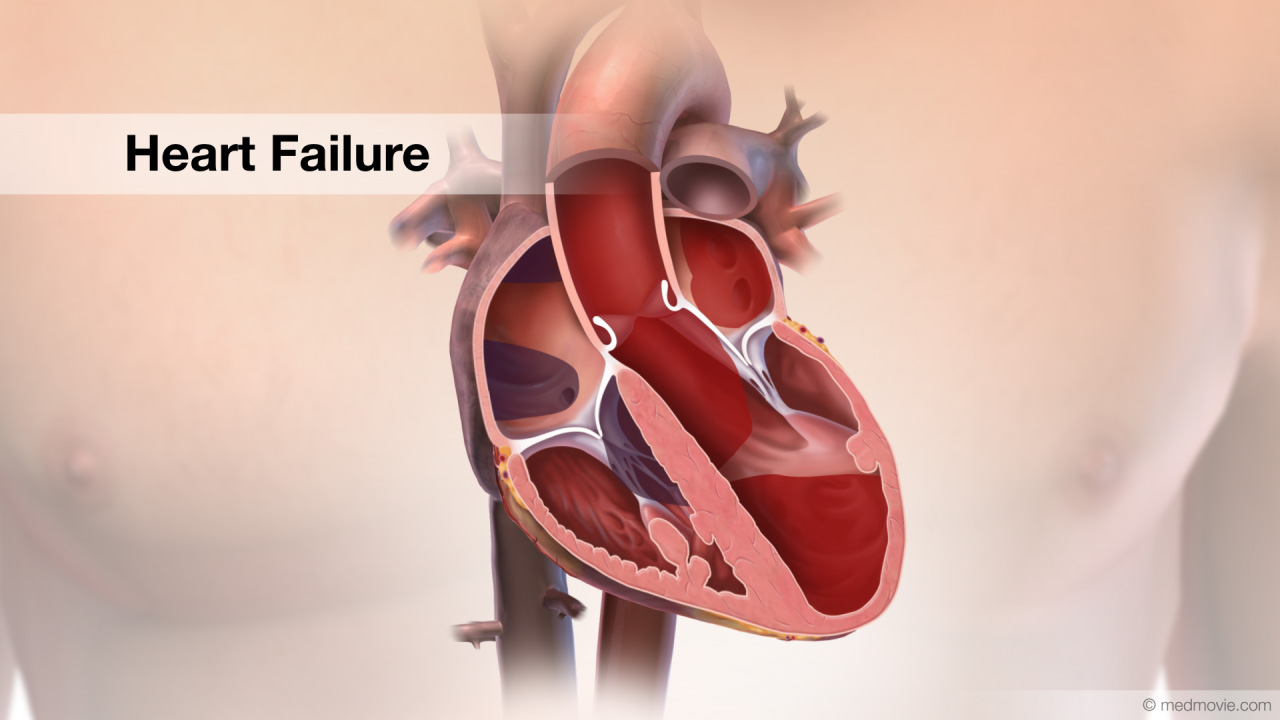 Heart FailureThe normal heart has strong muscular walls that pump blood out of the heart. Heart failure most often results from a…
Heart FailureThe normal heart has strong muscular walls that pump blood out of the heart. Heart failure most often results from a… Heart Lung BypassA heart-lung -or cardiopulmonary bypass - machine is used during heart surgery to deliver oxygenated blood to the body…
Heart Lung BypassA heart-lung -or cardiopulmonary bypass - machine is used during heart surgery to deliver oxygenated blood to the body…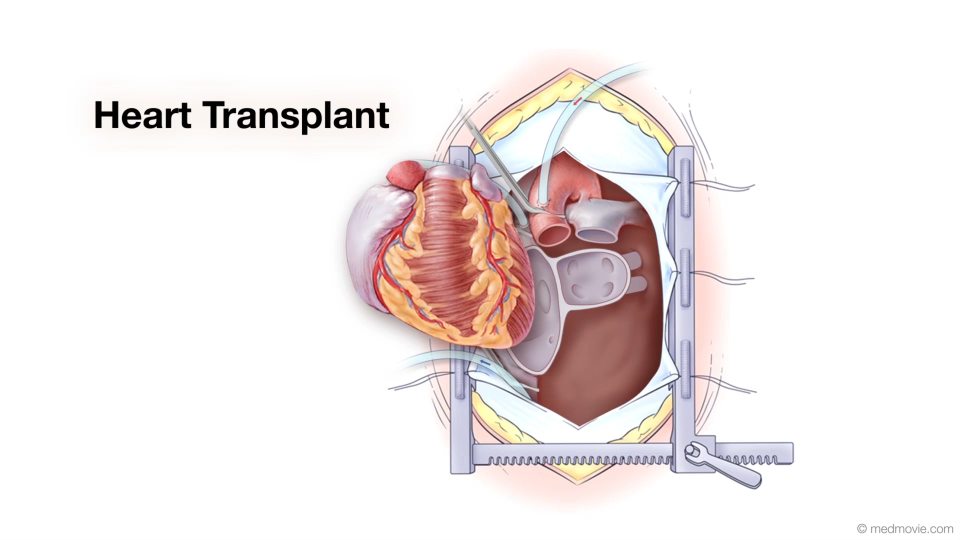 Heart TransplantA heart transplant is a surgical procedure that replaces a failing heart with a healthy donor heart. Physicians make a…
Heart TransplantA heart transplant is a surgical procedure that replaces a failing heart with a healthy donor heart. Physicians make a…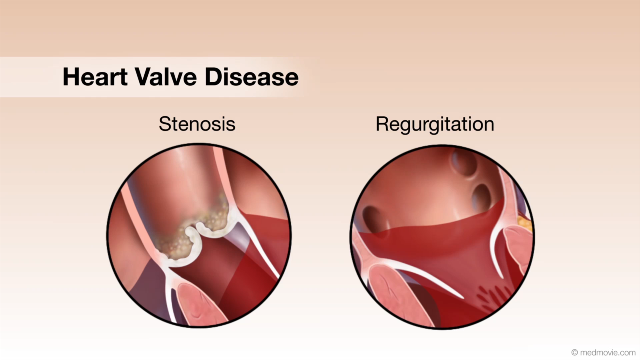 Heart Valve DiseaseValvular heart disease is any condition that disrupts the proper function of the valve. There are four valves in the…
Heart Valve DiseaseValvular heart disease is any condition that disrupts the proper function of the valve. There are four valves in the… Heart Valve SurgeryHeart valve replacement surgery replaces an abnormal or diseased heart valve with a healthy one.
There are four…
Heart Valve SurgeryHeart valve replacement surgery replaces an abnormal or diseased heart valve with a healthy one.
There are four…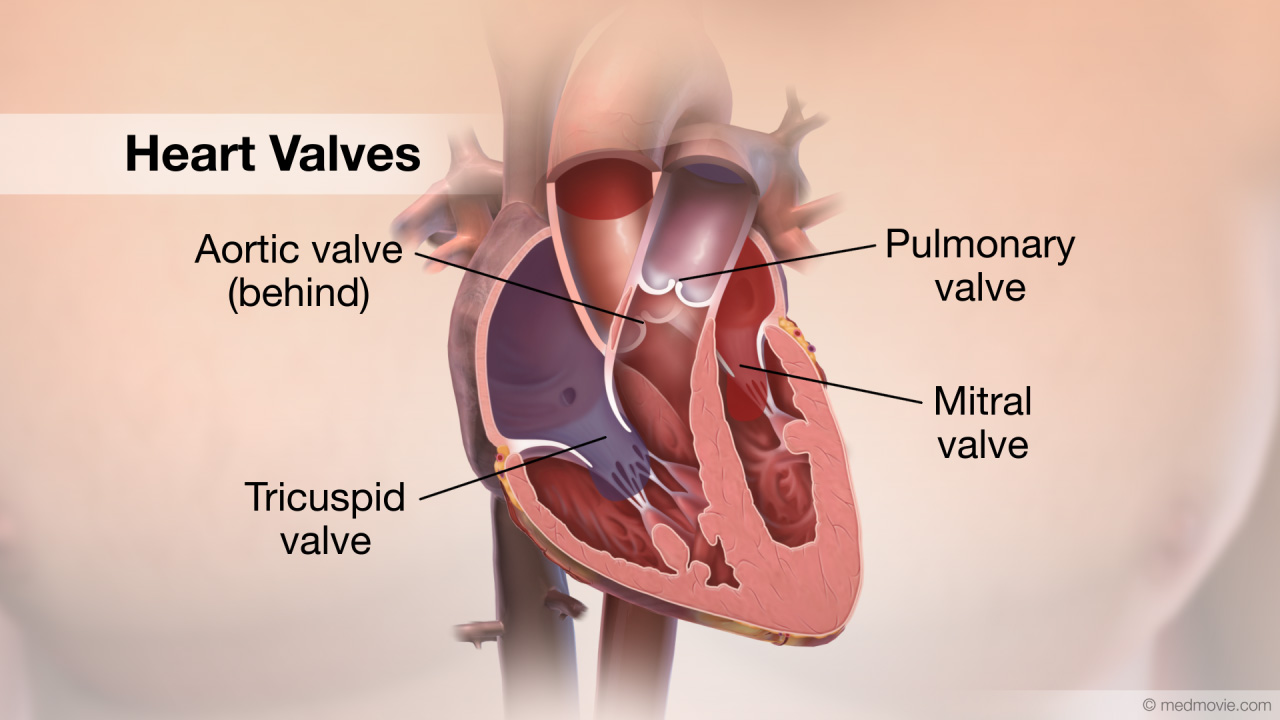 Heart ValvesThe heart has four valves. The mitral valve, the tricuspid valve, the pulmonary valve and the aortic valve. The mitral…
Heart ValvesThe heart has four valves. The mitral valve, the tricuspid valve, the pulmonary valve and the aortic valve. The mitral… High Blood PressureHigh blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition in which blood pressure levels are measured above the normal…
High Blood PressureHigh blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition in which blood pressure levels are measured above the normal… Hypertrophic CardiomyopathyThe normal heart has strong muscular walls that pump blood out of the heart.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a…
Hypertrophic CardiomyopathyThe normal heart has strong muscular walls that pump blood out of the heart.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a… Hypoplastic Left Heart SyndromeHypoplastic left heart syndrome is the result of underdevelopment of the left heart structures and includes a tiny, or…
Hypoplastic Left Heart SyndromeHypoplastic left heart syndrome is the result of underdevelopment of the left heart structures and includes a tiny, or… ICD DeviceAn Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, or ICD, is a battery-powered device that keeps track of your heartbeat, and…
ICD DeviceAn Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, or ICD, is a battery-powered device that keeps track of your heartbeat, and… ICD OverviewAn Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, or ICD, is a battery-powered device that keeps track of your heartbeat and…
ICD OverviewAn Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, or ICD, is a battery-powered device that keeps track of your heartbeat and…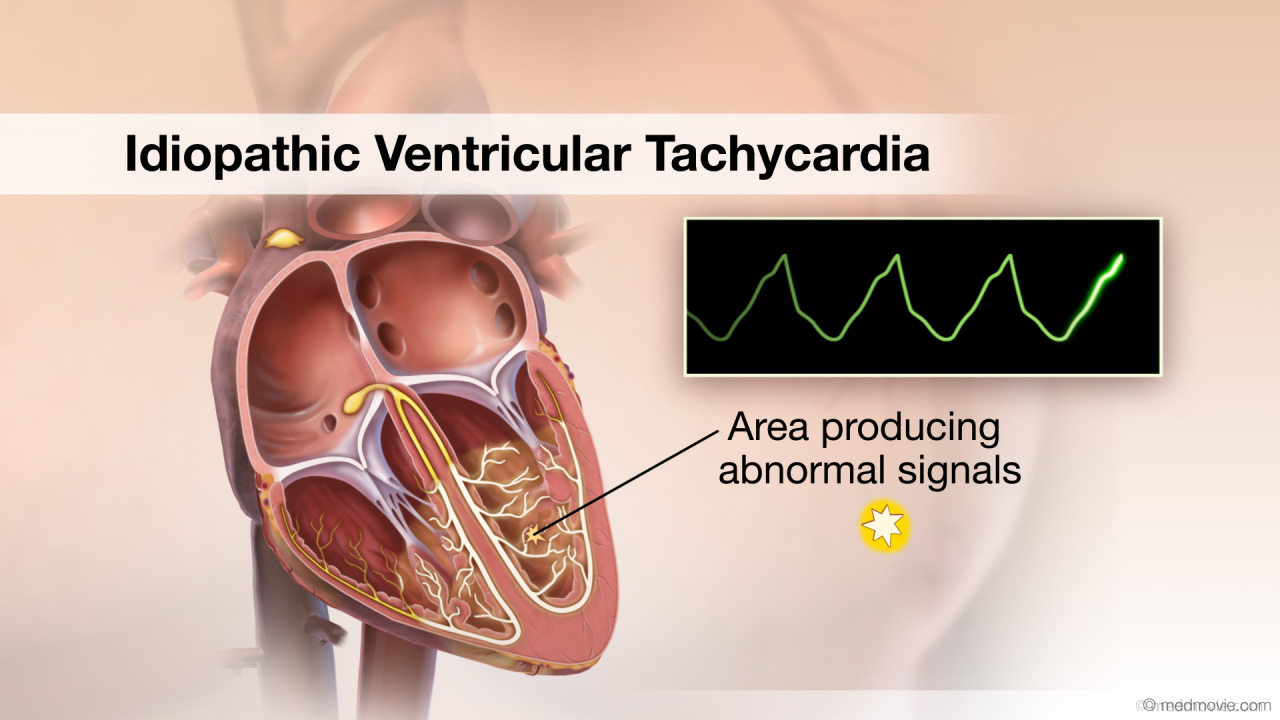 Idiopathic Ventricular TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
Idiopathic Ventricular TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…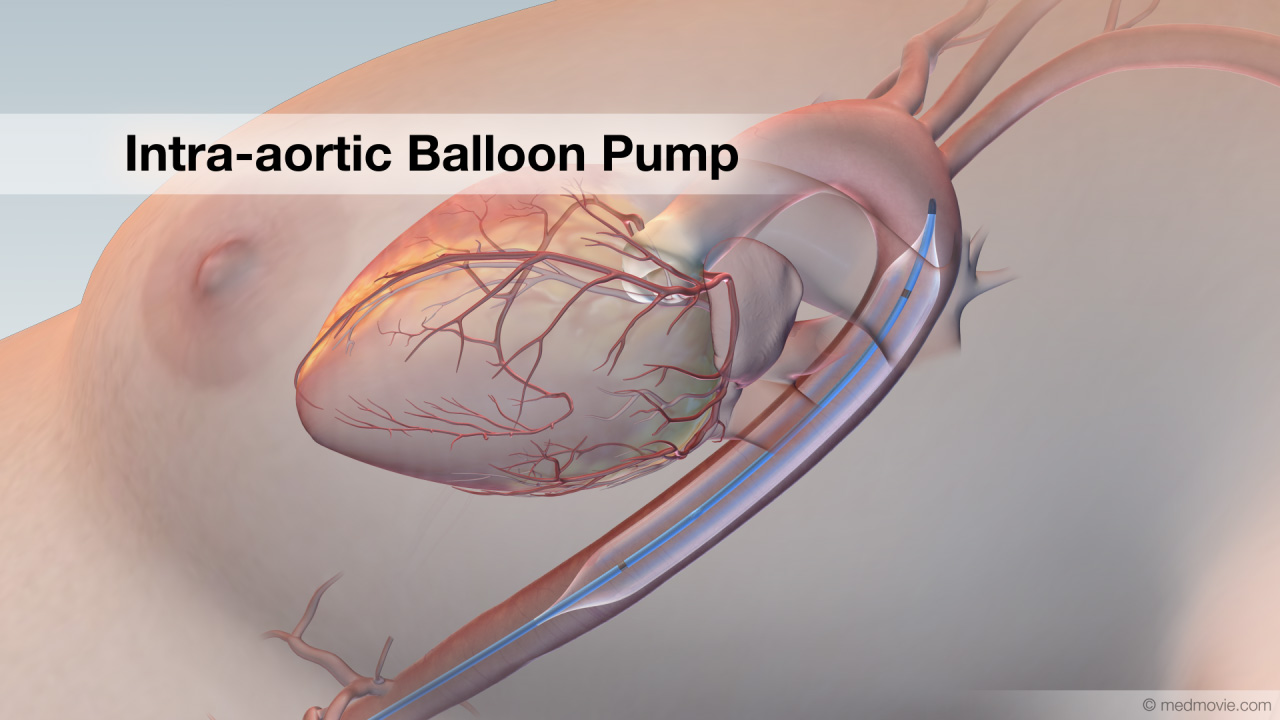 Intra-aortic BalloonAn intra-aortic balloon pump or IABP is an inflatable balloon that is surgically implanted into the aorta to help the…
Intra-aortic BalloonAn intra-aortic balloon pump or IABP is an inflatable balloon that is surgically implanted into the aorta to help the… Ischemic Ventricular TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
Ischemic Ventricular TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…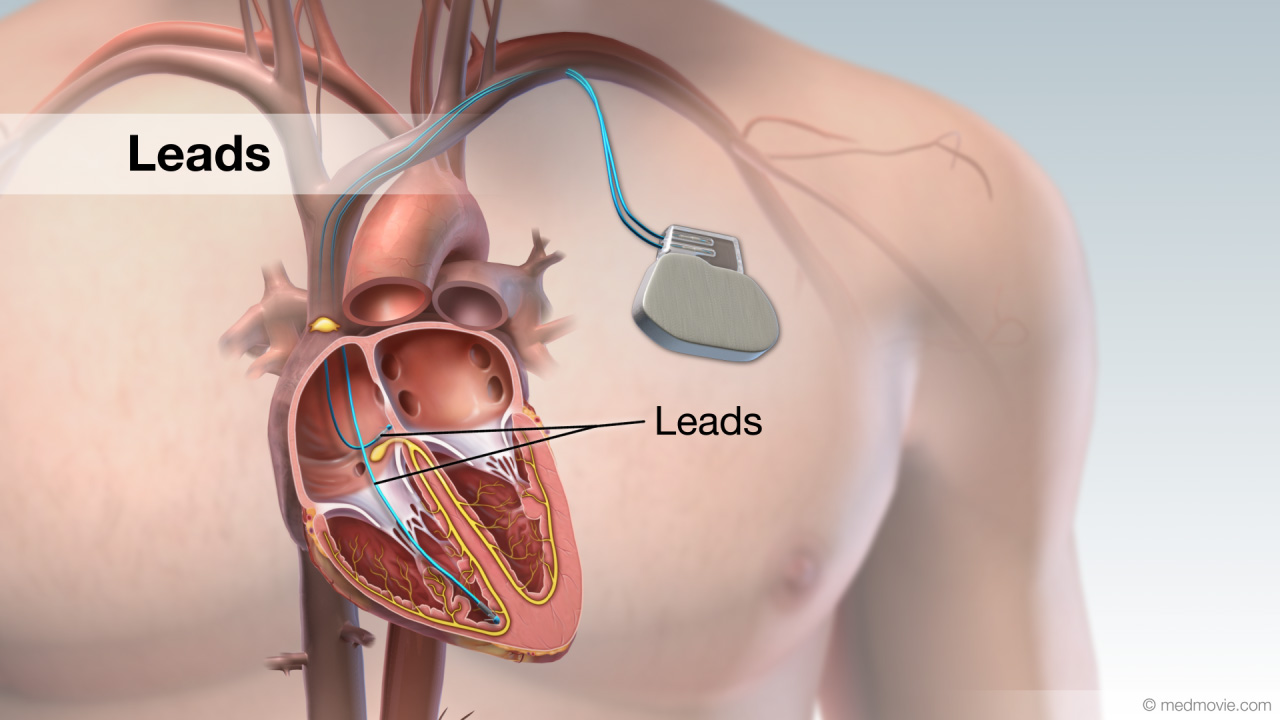 LeadA lead is a device that measures the passage of electrical signals. Leads are used in electrocardiograms to record the…
LeadA lead is a device that measures the passage of electrical signals. Leads are used in electrocardiograms to record the…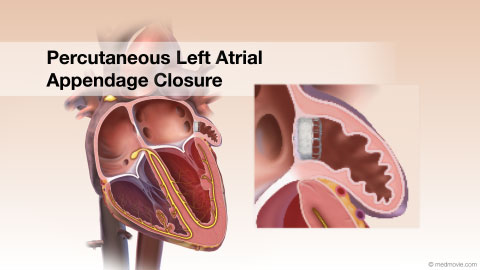 LAACA left atrial appendage closure device can be used for atrial fibrillation patients to help prevent strokes and as an…
LAACA left atrial appendage closure device can be used for atrial fibrillation patients to help prevent strokes and as an… Long QT SyndromeLong QT Syndrome is a condition that is characterized by a delay in repolarization of the heart after the initial…
Long QT SyndromeLong QT Syndrome is a condition that is characterized by a delay in repolarization of the heart after the initial… Mitral Valve ClipA mitral valve clip is a device that supports an improperly functioning mitral valve.
Mitral valve leaflets that do…
Mitral Valve ClipA mitral valve clip is a device that supports an improperly functioning mitral valve.
Mitral valve leaflets that do…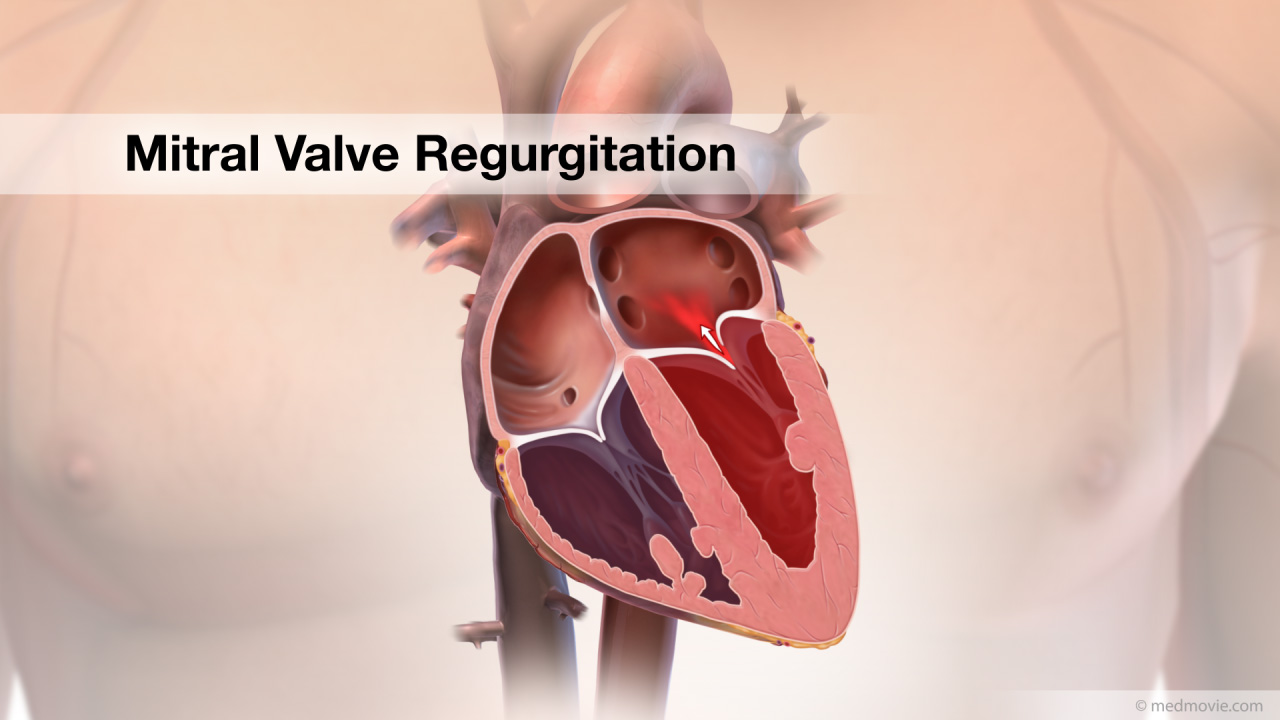 Mitral RegurgitationThe heart has four valves that regulate blood flow through the heart. The mitral valve is the heart valve located…
Mitral RegurgitationThe heart has four valves that regulate blood flow through the heart. The mitral valve is the heart valve located…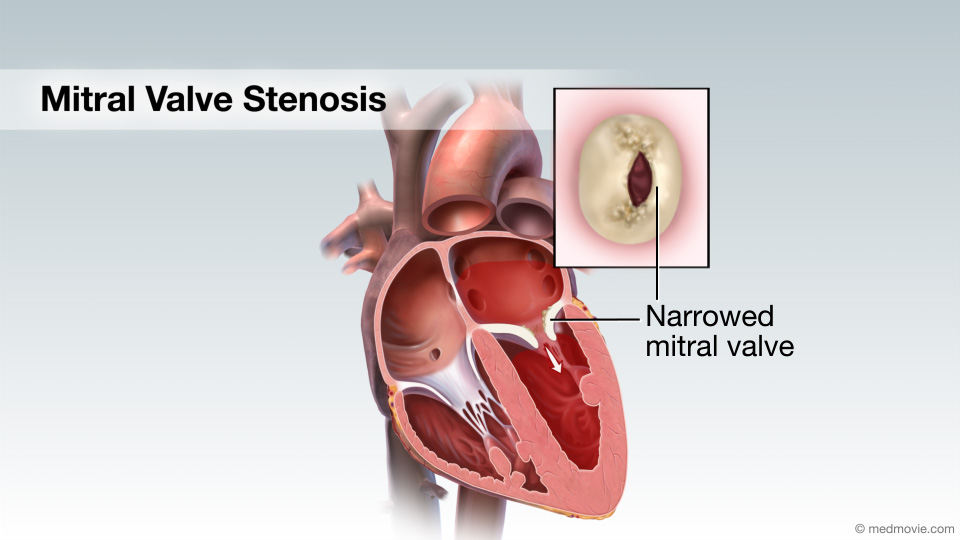 Mitral Valve StenosisMitral valve stenosis is a condition when the mitral valve does not open properly, narrowing the opening, reducing the…
Mitral Valve StenosisMitral valve stenosis is a condition when the mitral valve does not open properly, narrowing the opening, reducing the…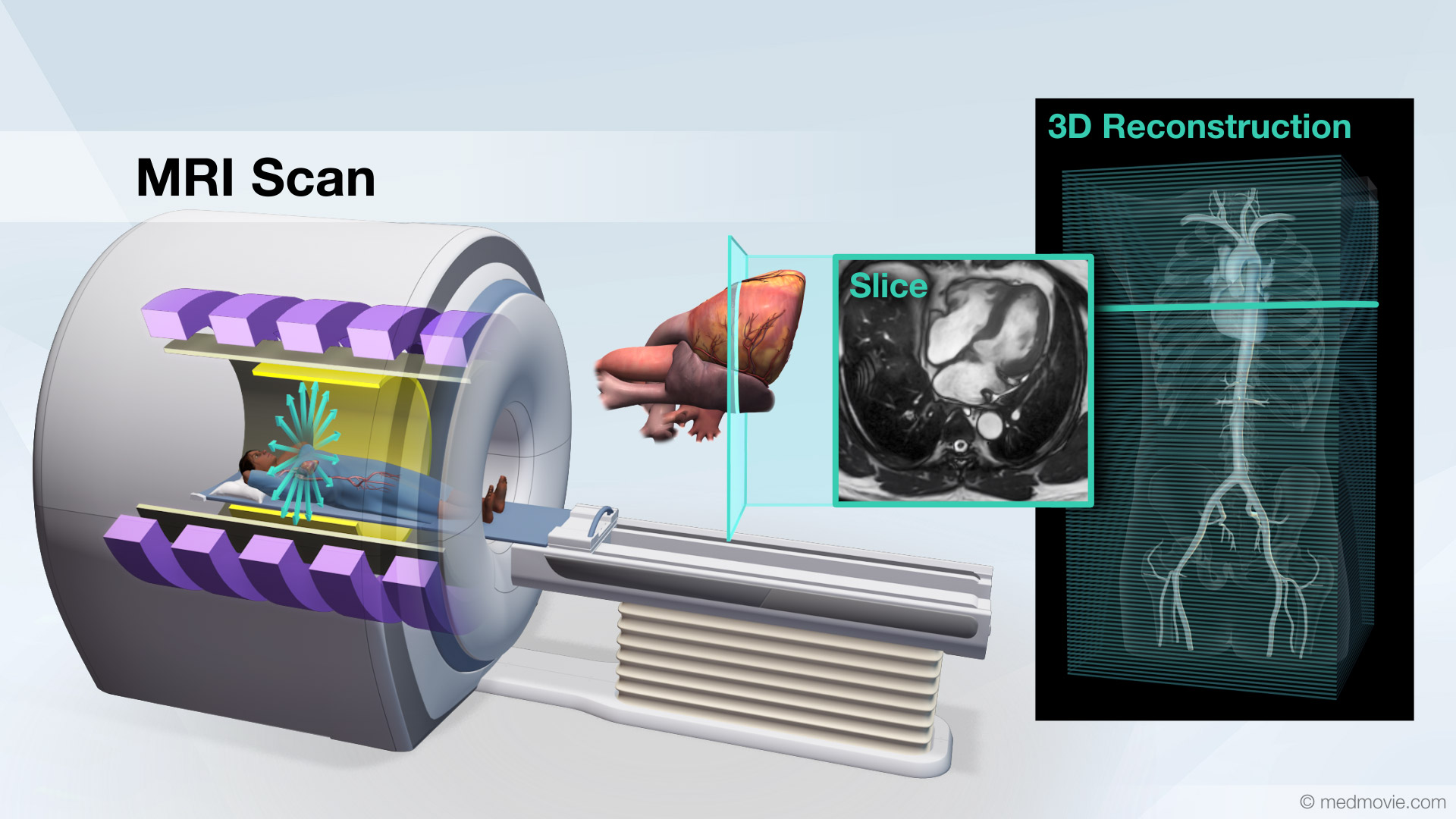 MRI ScanA Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan, or MRI scan, is a non-invasive diagnostic test that uses a magnetic field and radio…
MRI ScanA Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan, or MRI scan, is a non-invasive diagnostic test that uses a magnetic field and radio…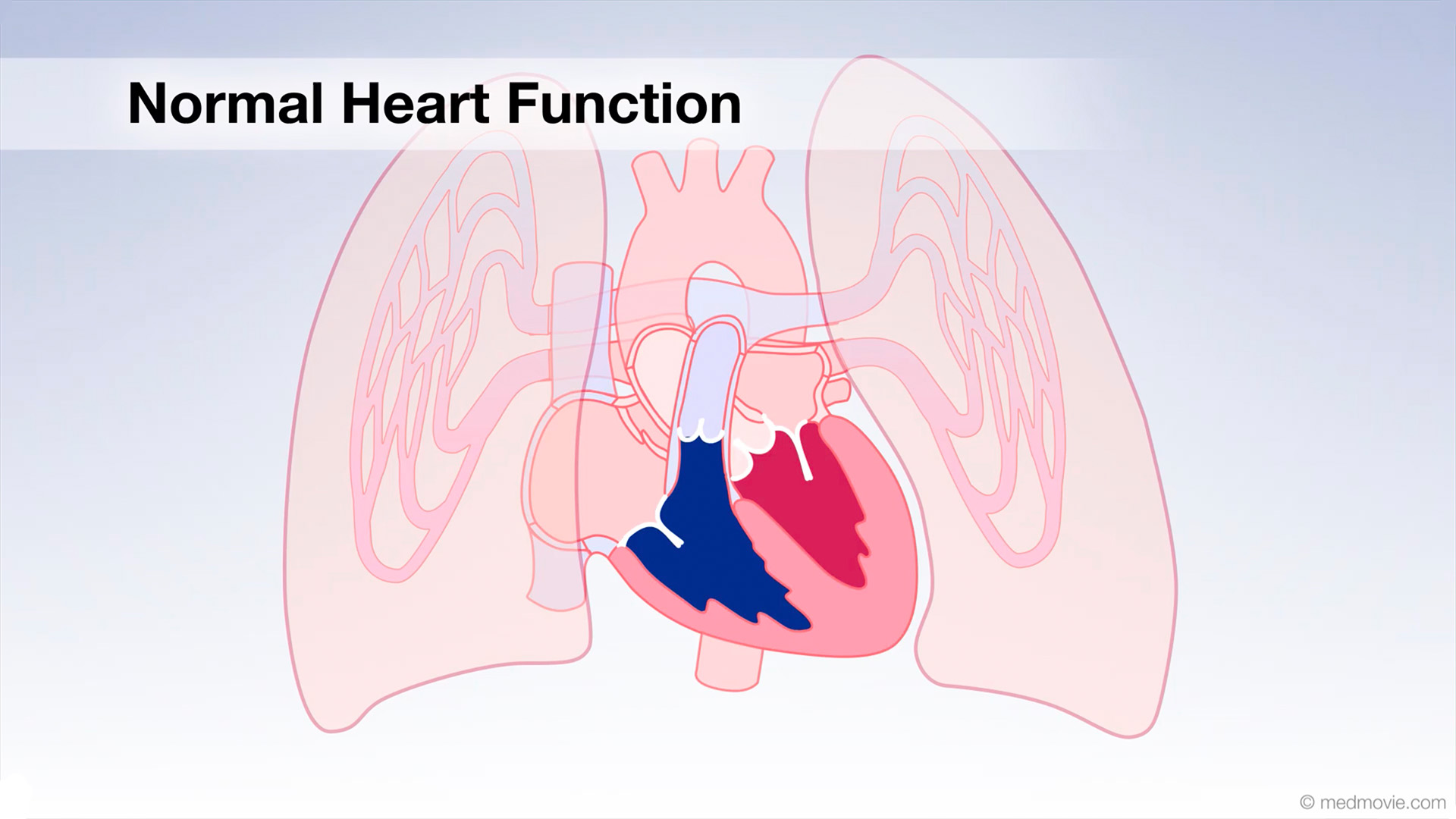 Normal Heart FunctionBlood flows through the heart in a specific pattern in order to pump deoxygenated, or blue blood to the lungs and…
Normal Heart FunctionBlood flows through the heart in a specific pattern in order to pump deoxygenated, or blue blood to the lungs and…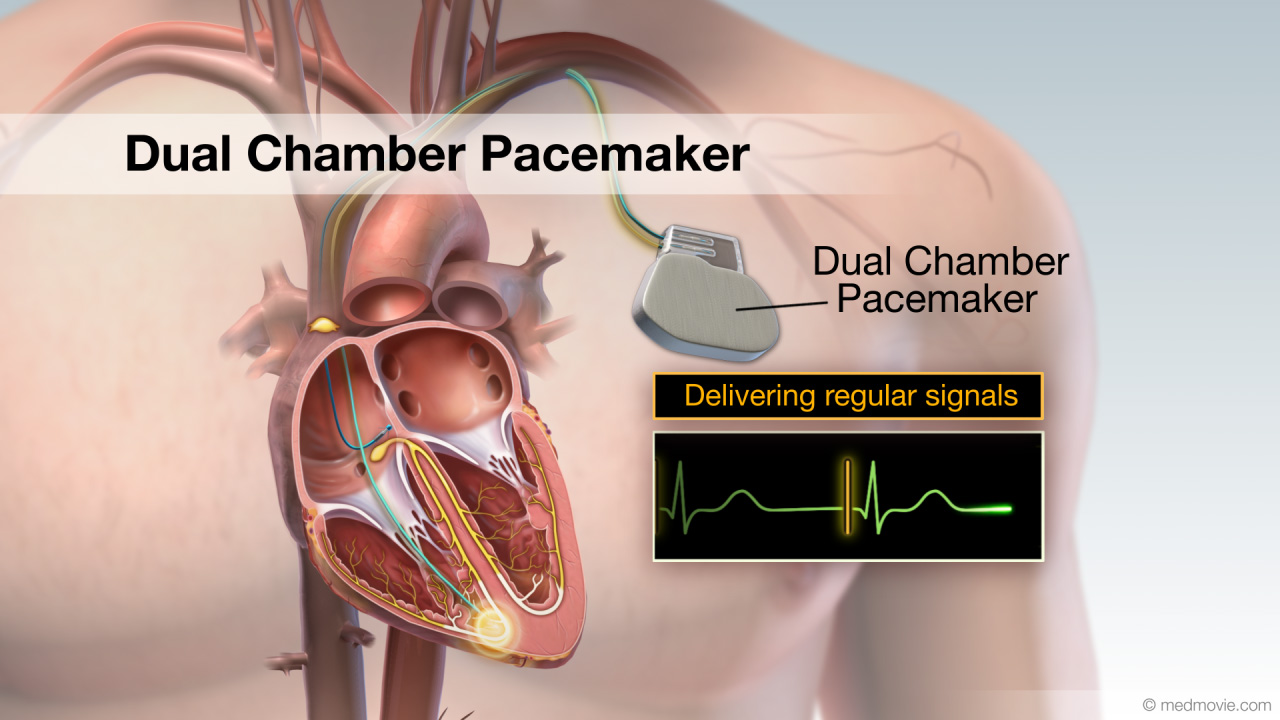 Pacemaker - Dual ChamberA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or…
Pacemaker - Dual ChamberA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or…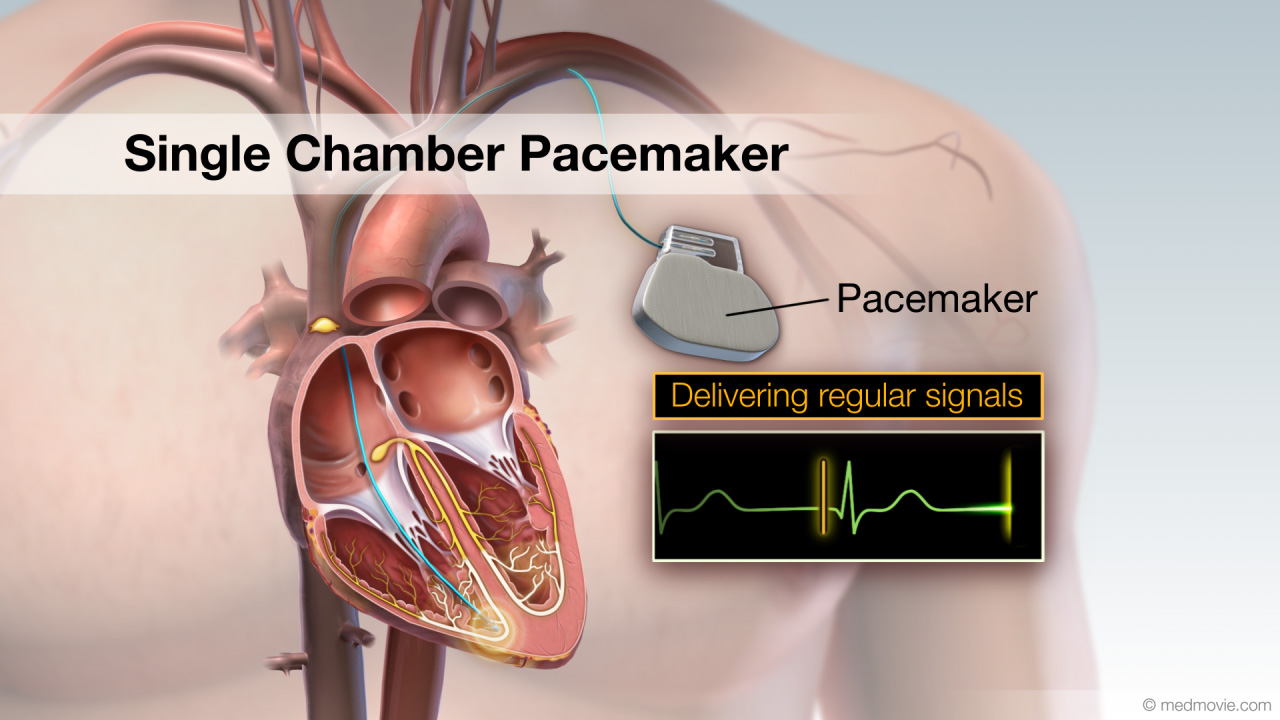 Pacemaker - Single ChamberA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or…
Pacemaker - Single ChamberA pacemaker is a battery-powered device that sends electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a proper rate or…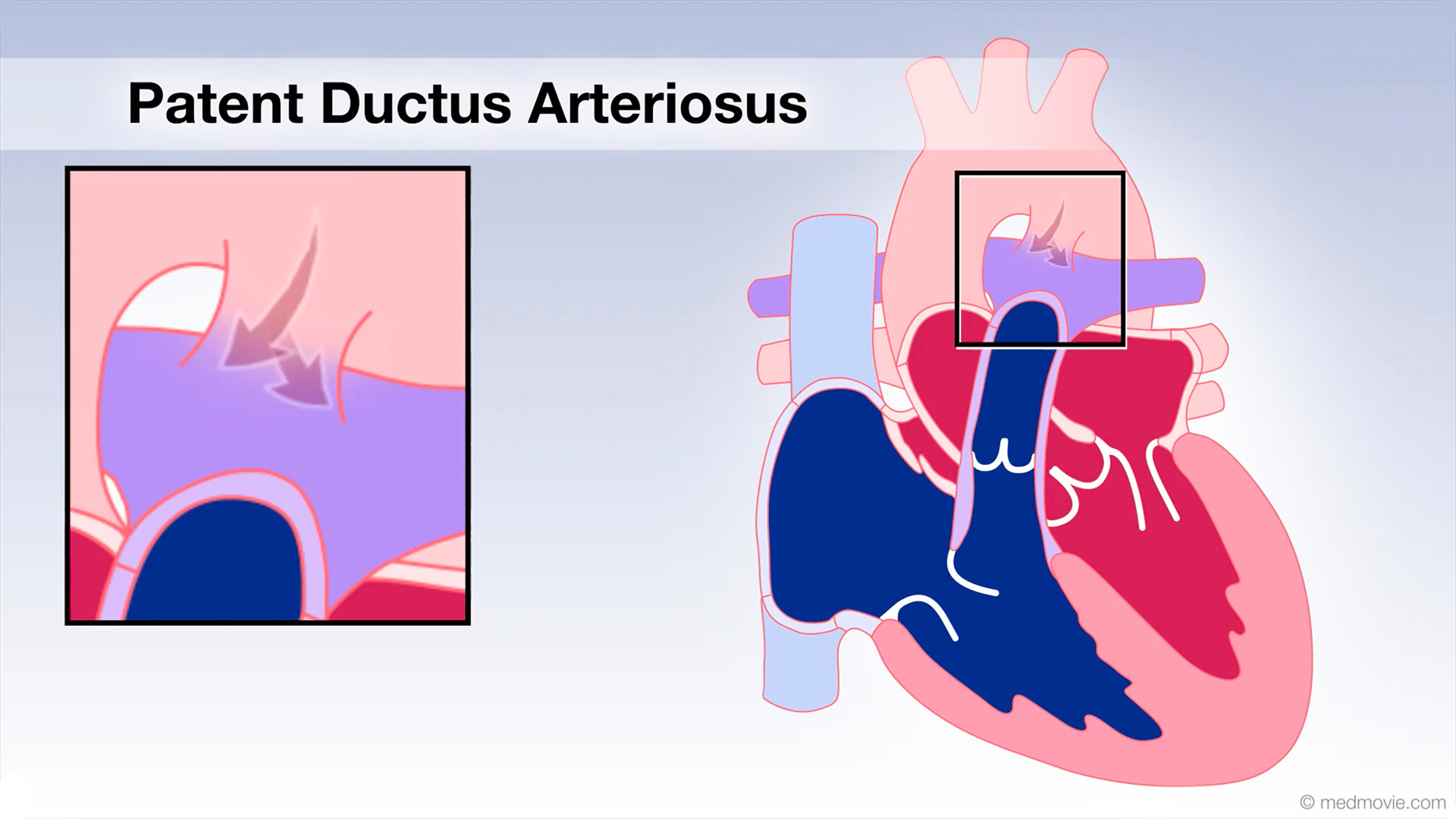 Patent Ductus Arter.The ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel that connects the blood vessel going to the lungs, known as the pulmonary…
Patent Ductus Arter.The ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel that connects the blood vessel going to the lungs, known as the pulmonary… PET ScanA Positron Emission Tomography scan, or PET scan, is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses small amounts of a…
PET ScanA Positron Emission Tomography scan, or PET scan, is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses small amounts of a… Physical ActivityA sedentary lifestyle is one of the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease. A sedentary lifestyle is…
Physical ActivityA sedentary lifestyle is one of the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease. A sedentary lifestyle is…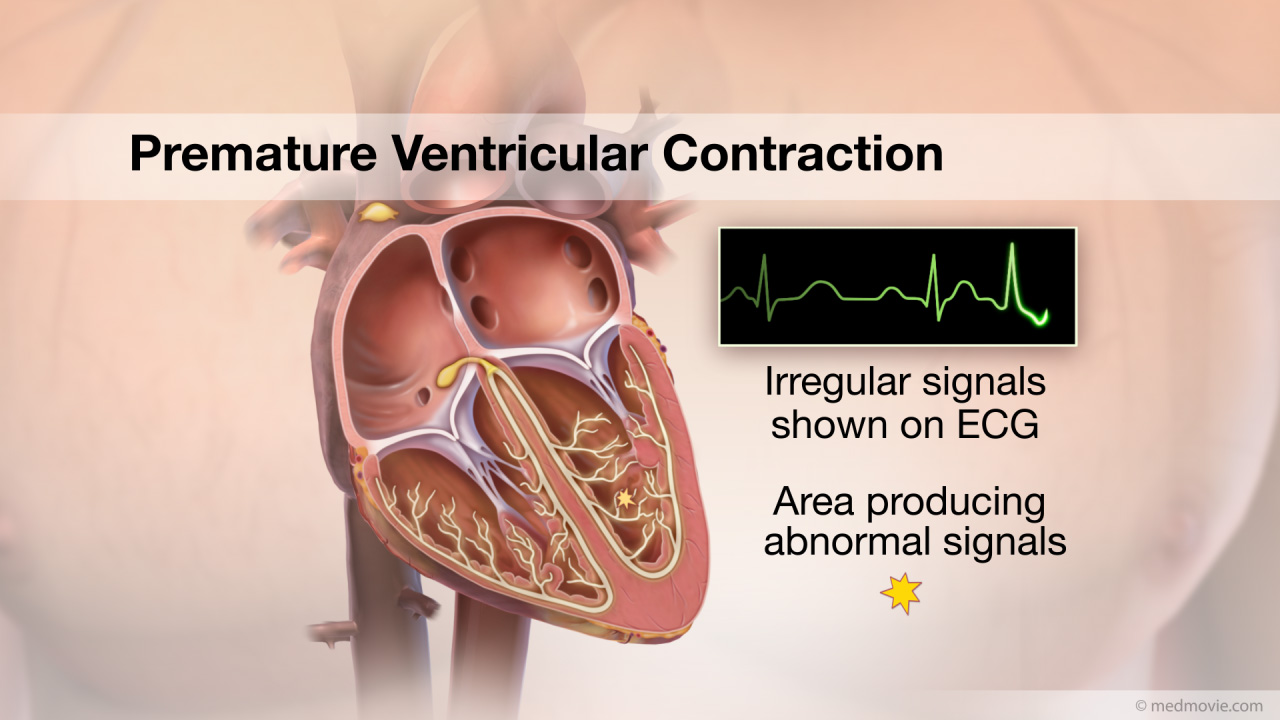 PVCThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
PVCThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell… Pulm. Valve StenosisThe pulmonary valve is located between the right ventricle and the large blood vessel to the lungs which is called the…
Pulm. Valve StenosisThe pulmonary valve is located between the right ventricle and the large blood vessel to the lungs which is called the… Quitting SmokingQuitting smoking is not easy, but there are things you can do to increase your chances of success. Planning strategies…
Quitting SmokingQuitting smoking is not easy, but there are things you can do to increase your chances of success. Planning strategies… RVOT Ventricular TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
RVOT Ventricular TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell… Sinus RhythmA normal heartbeat produces a regular, identifiable pattern: the P wave, the QRS complex, and the T wave. These…
Sinus RhythmA normal heartbeat produces a regular, identifiable pattern: the P wave, the QRS complex, and the T wave. These… Sinus TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made of several parts that tell the…
Sinus TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made of several parts that tell the…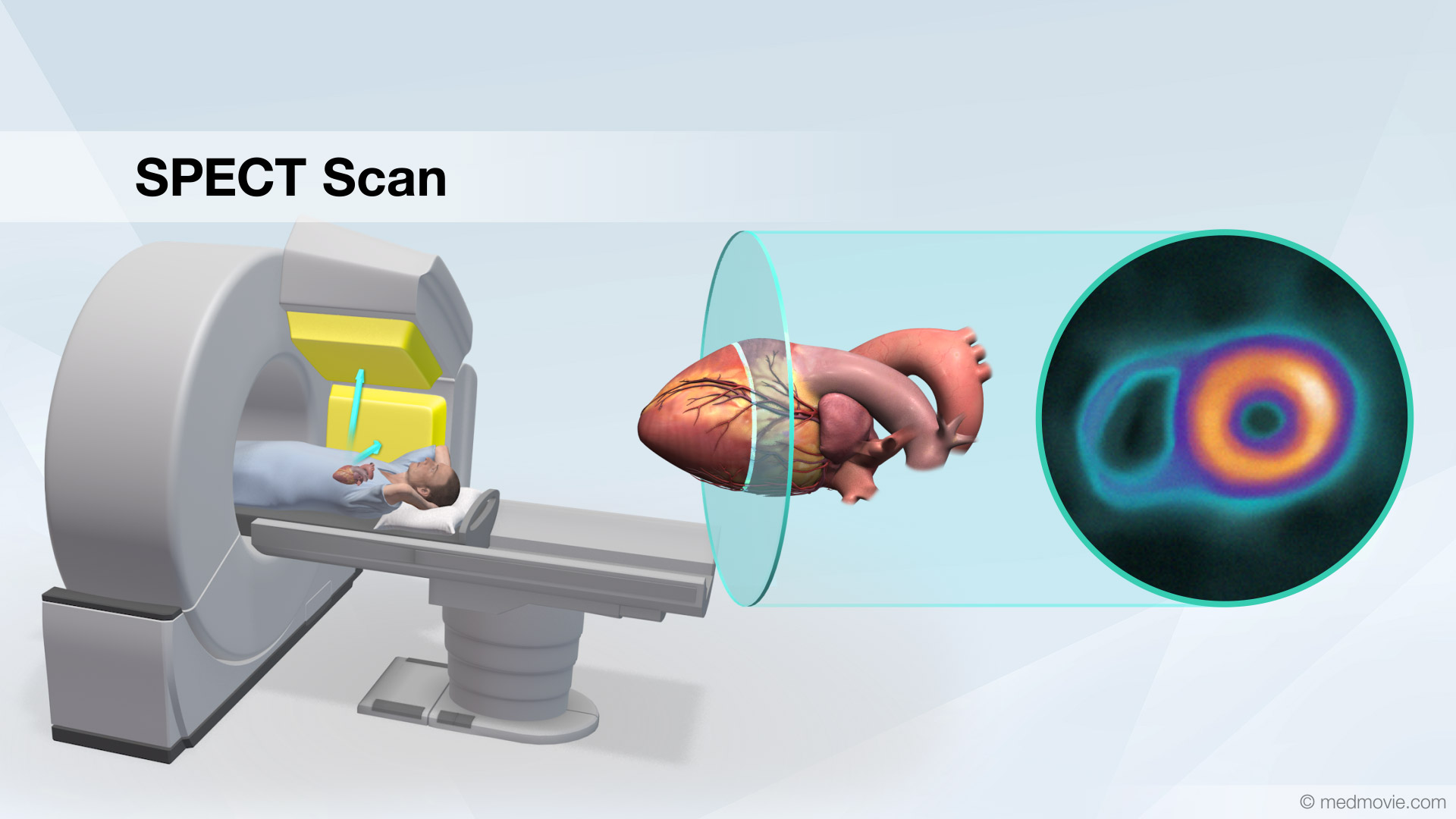 SPECT ScanA Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography scan, or SPECT scan, is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses…
SPECT ScanA Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography scan, or SPECT scan, is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses…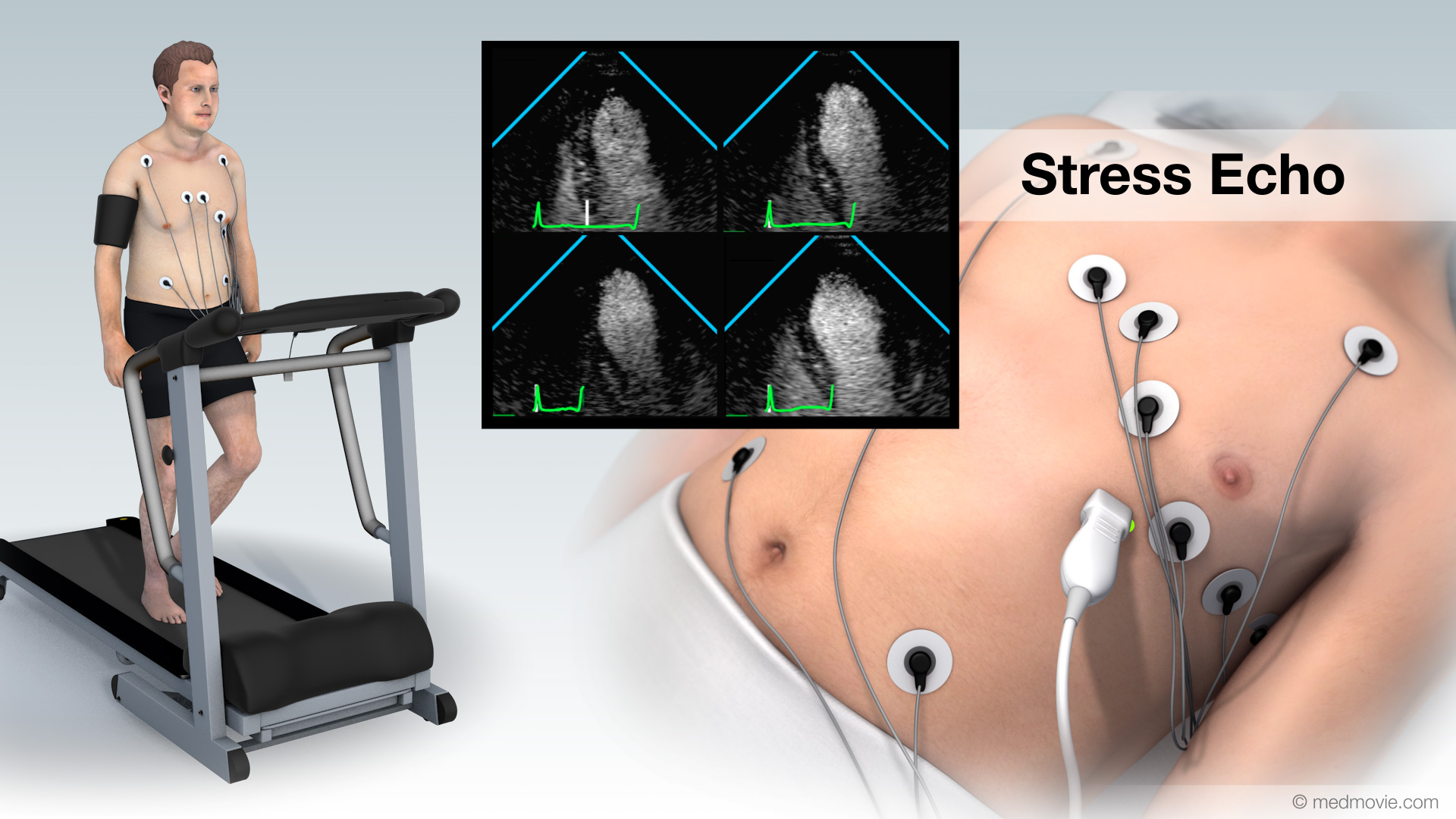 Stress EchoA stress echo, also called an exercise heart ultrasound is used to evaluate heart function by combining an exercise…
Stress EchoA stress echo, also called an exercise heart ultrasound is used to evaluate heart function by combining an exercise… Sudden Cardiac ArrestSudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is an event caused by a problem with the heart's "electrical" system. SCA occurs when the…
Sudden Cardiac ArrestSudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is an event caused by a problem with the heart's "electrical" system. SCA occurs when the… SVTThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
SVTThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell… Supraventricular Tachycardia OverviewSupraventricular tachycardias are heart conditions with a fast heart rhythm and an electrical abnormality of the atria…
Supraventricular Tachycardia OverviewSupraventricular tachycardias are heart conditions with a fast heart rhythm and an electrical abnormality of the atria… Transcatheter Aortic Valve ReplacementTranscatheter aortic valve replacement, or TAVR, is a treatment for aortic valve stenosis, which is a narrowing of the…
Transcatheter Aortic Valve ReplacementTranscatheter aortic valve replacement, or TAVR, is a treatment for aortic valve stenosis, which is a narrowing of the…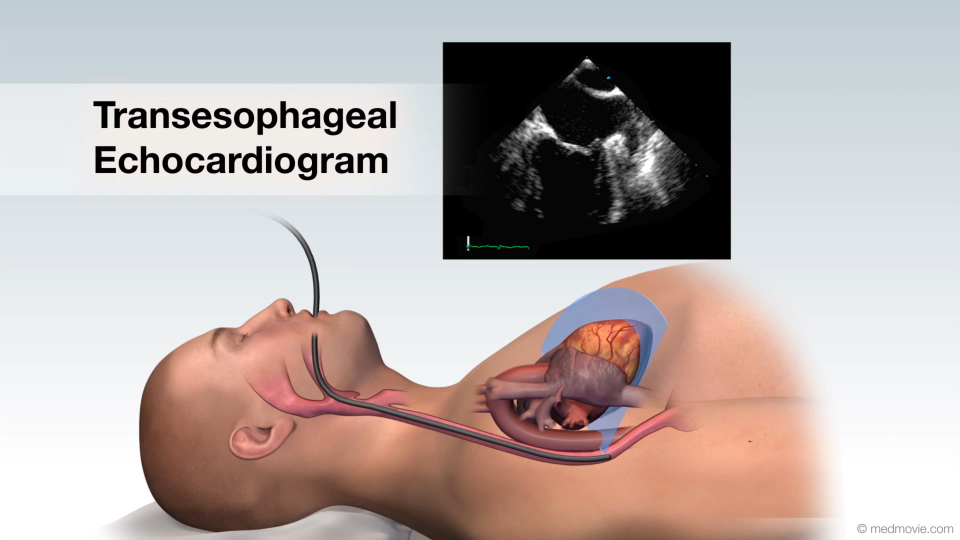 Transesophageal EchocardiogramA transesophageal echocardiogram is a diagnostic test used to view the structures of the beating heart. In this…
Transesophageal EchocardiogramA transesophageal echocardiogram is a diagnostic test used to view the structures of the beating heart. In this…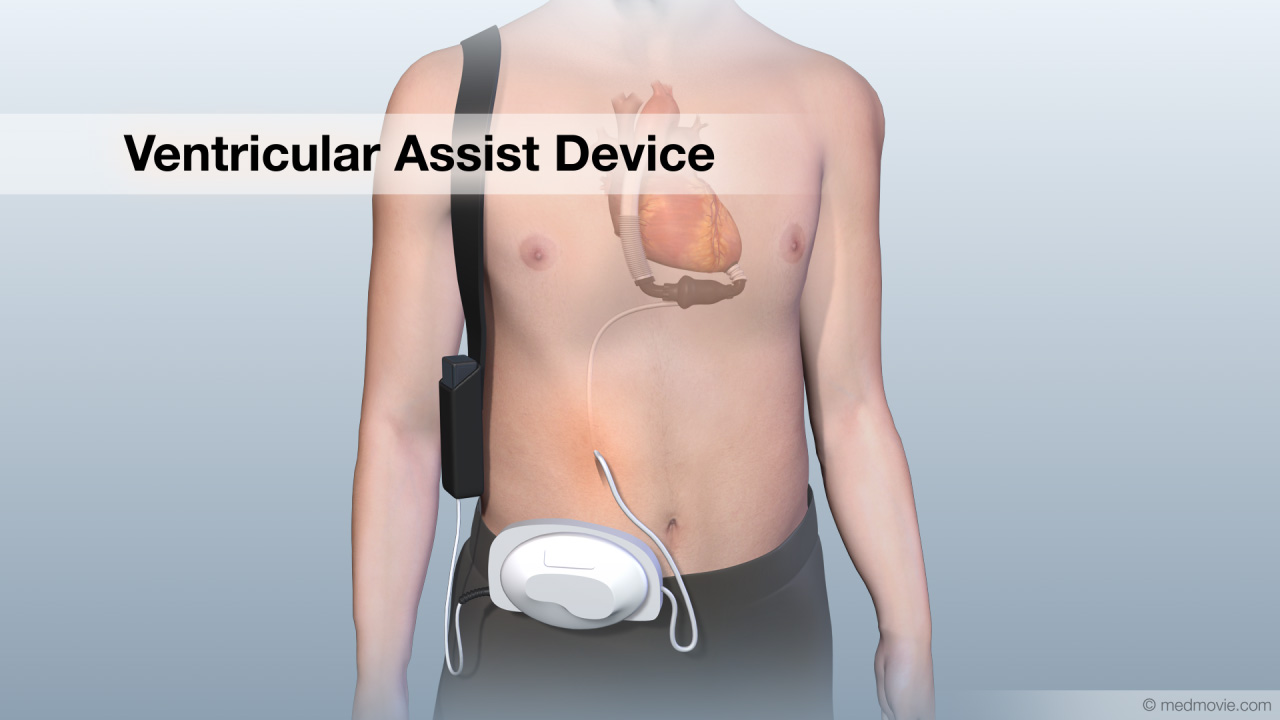 Ventricular Assist DeviceA ventricular assist device, VAD, is a pumping device that is used to help a heart that can no longer pump blood…
Ventricular Assist DeviceA ventricular assist device, VAD, is a pumping device that is used to help a heart that can no longer pump blood… Ventricular FibrillationThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…
Ventricular FibrillationThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made up of several parts that tell…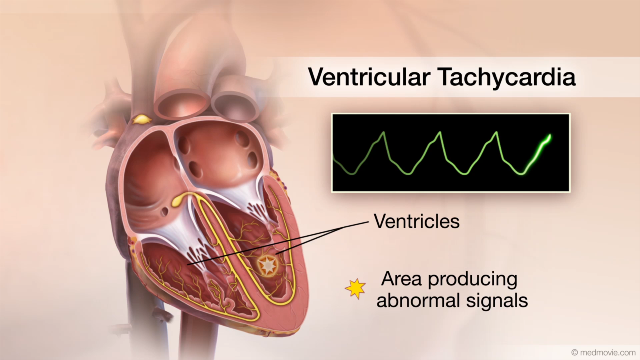 Ventric. TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made of several parts that tell the…
Ventric. TachycardiaThe heartbeat is controlled by the electrical system of the heart. This system is made of several parts that tell the…